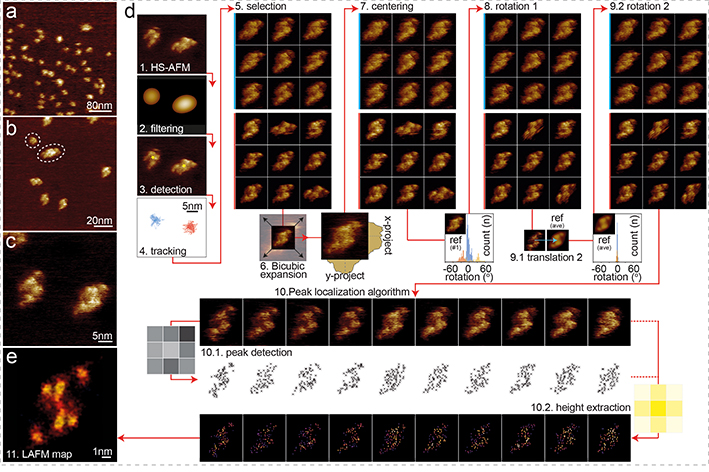
Figure 3). HS-AFM imaging and LAFM workflow of CLC-ec1.
HS-AFM images of CLC-ec1 in a POPE:POPG (2:1, w:w) membrane at (a) 400nm (300 pixels), (b) 120nm (300 pixels) and (c) 40nm (300 pixels) image (frame) size of predominantly dimeric CLC-ec1 at low density in a membrane. (d) LAFM method workflow steps: 1) HS-AFM movie acquisition 2) Image Gaussian filtering. 3) Molecule detection. 4) 2D-tracking to separate single molecules (molecules highlighted blue or red could be treated individually). 5) Molecule selection. 6) Bicubic expansion (original pixel sampling: 1.33Å/p, expanded pixel sampling: 0.5Å/p). 7) Molecule centering (1st round) by center of mass. 8) Rotational alignment (1st round) of molecules through rotational cross-correlation with a reference frame. 9) Translational and rotational alignment (2nd round) through cross-correlation with the average molecule from step 8 (inset histograms: rotation angles distributions for all particle in steps 8 and 9). 10) LAFM method: Input: aligned HS-AFM images (n = 200). 10.1) LAFM peak detection of local maxima. 10.2) Height extraction at each peak position and application of a 1.4Å localization probability distribution. 11) LAFM map reconstruction through merging of all LAFM detections.