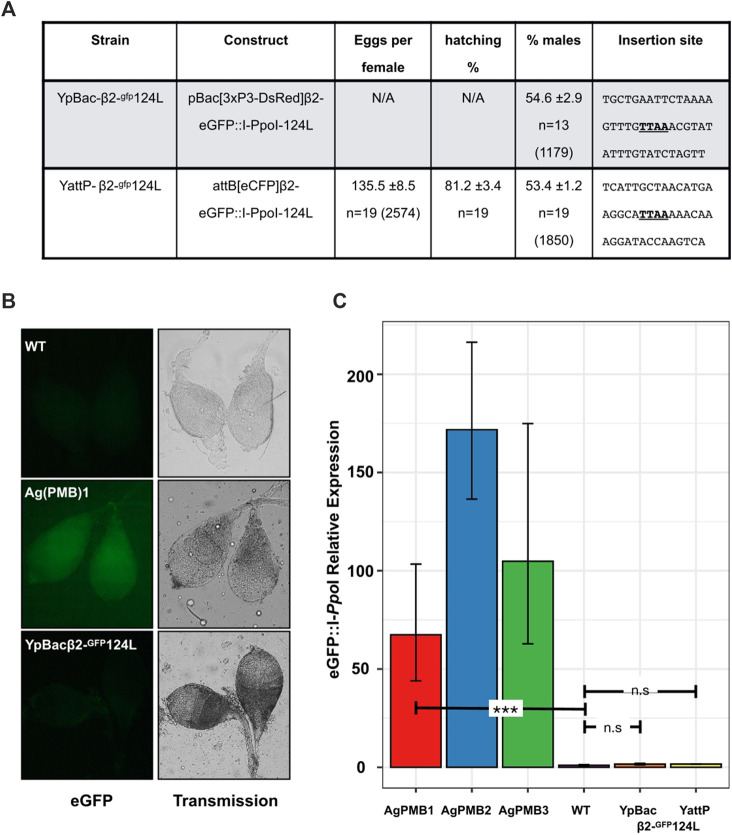
FIGURE 2.
Transcriptional suppression of Y-linked X-shredder constructs abolishes sex ratio distortion. (A) Progeny analysis of males from the two Y linked X-shredder strains crossed to wild-type females. Shown is the average number of eggs laid per n females analyzed (±represents the standard error of the mean; SEM). Average percentage of larvae hatching from the eggs (±SEM), from n females analyzed. Average percentage of males in the progeny (±SEM) from n females. The total number of eggs or individuals counted in each experiment is given in parentheses. Sequences (20 bp each side) flanking the PB integration site (TTAA) of the transformation constructs are also shown. (B) eGFP fluorescence from dissected wild type (WT), Ag(PMB)1 and YpBac-β2-gfp124L testis. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR showing the relative expression of eGFP:I-PpoI variants in autosomal X-shredder strains [Ag(PMB)1-3] and Y-linked X-shredder strains. Expression levels were normalized to G3 wild-type (RQ = 1) which contains no I-PpoI component. Expression of the X-shredder is undetectable in both Y-chromosome insertions compared to G3 wild-type (unpaired t-test p = 0.1669 for YpBac and p = 0.2509 for YattP). Expression levels from autosomal strains, Ag(PMB)1 (unpaired t-test p = 0.0078), Ag(PMB)2 (originally W124L-3) and Ag(PMB)3 (originally L111A-2) which led to sex ratio distortion are shown.