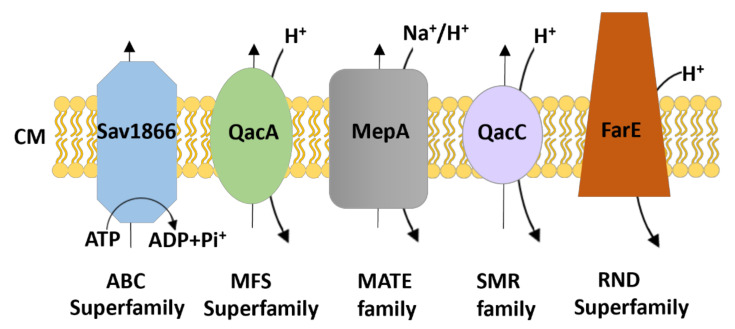
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the families/superfamilies of multidrug exporters in staphylococci. Each transport system is depicted as a distinct shape and colour along with the energy source for driving substrate export (i.e., ATP hydrolysis for the ABC superfamily and electrochemical energy stored in the ion gradient [H+/Na+] for the others). The transporters classified within the ATP-binding cassette (ABC), major facilitator superfamily (MFS), multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE), small multidrug resistance (SMR), and resistance-nodulation division (RND) family commonly expel their substrates across the cytoplasmic membrane (CM). Examples of S. aureus transporters are included.