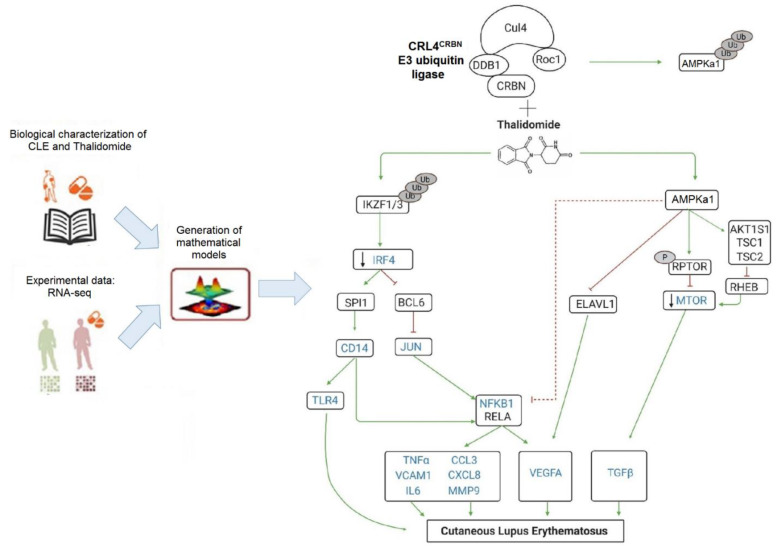
Figure 2.
Proposed thalidomide mechanism of action in Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (CLE). On the one hand, in the presence of thalidomide, CRL4CRBN complex ubiquitinates IKZF1/3 promoting downstream modulation of IRF4 and, on the other hand, prevents the ubiquitination of AMPKa1, increasing the expression of phosphorylated RPTOR which in turn inhibits mTOR signaling. Therefore, thalidomide modulates IRF4 and AMPK/mTOR pathways and their downstream effector molecules contributing to the resolution of inflammatory lesions in CLE.