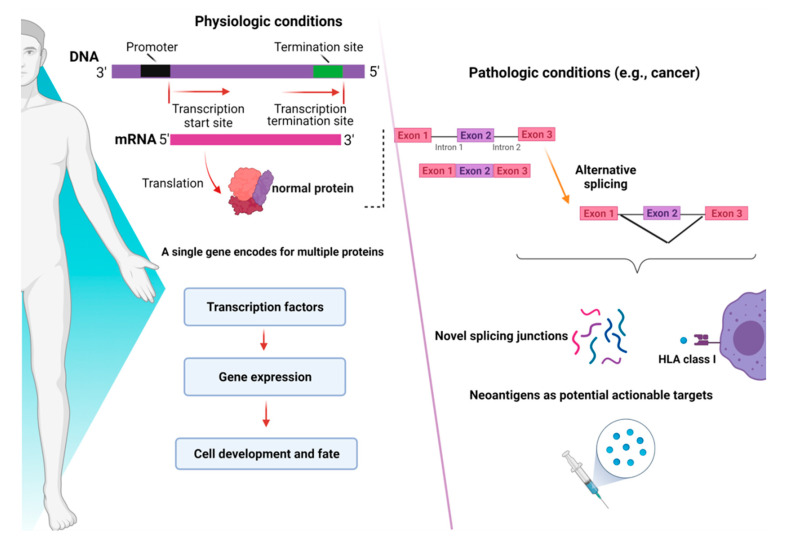
Figure 2.
Consequences of alternative splicing in physiologic and pathologic conditions. In physiologic conditions (left panel), alternative splicing serves as a modulator of gene expression and regulates the function of transcriptional factors, ultimately dictating cell development and fate. In pathologic conditions (right panel), alternative splicing can produce novel junctions that, when exclusive to tumor cells, might represent actionable targets for immunotherapy. Images were generated (in part) using BioRender.