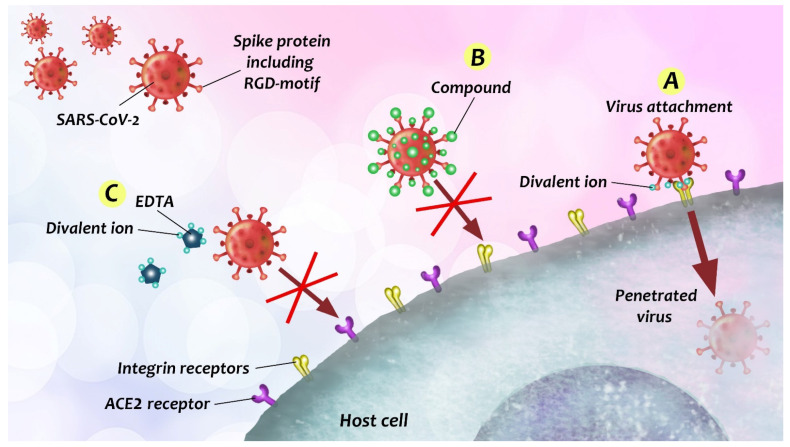
Figure 9.
Schematic illustration of SARS-CoV-2 attachment and two possible examples of ways to inhibit this process. (A) Virus can attach to ACE2 receptor or integrins of the host cell. RGD-integrin interaction occurs in calcium-dependent manner [274]. As the result of the process, the virus penetrates into the cell and starts to copy itself. (B) Several compounds bind to the spike protein or even may alter it [275] and prevent virus-receptor attachment. (C) Lowering divalent ion concentrations in the lungs with pulmonary EDTA chelation therapy may inhibit virus-host interaction [274].