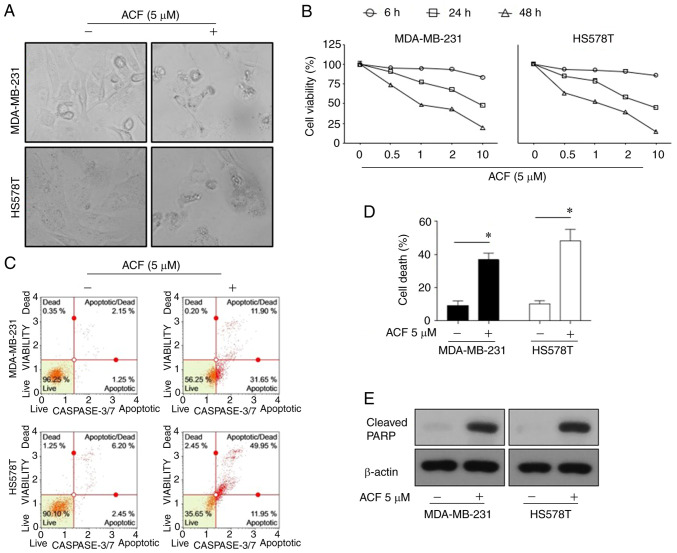
Figure 1.
Apoptosis is promoted by (ACF) in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines in a time and dose-dependent manner. (A) Microscopic images (magnification, ×100) of MDA-MB-231 and HS578T cells. (B) Effects of ACF on the viability of MDA-MB-231 and HS578T cells. The cells were treated with various concentrations (0, 0.5, 1, 2 and 10 µM) of ACF for 6, 24 and 48 h, and cell viability was determined using the sulforhodamine B assay. (C) MDA-MB-231 and HS578T cells were treated with 0 or 5 µM ACF for 24 h. Caspase-3/7 activity was analyzed using Muse Caspase-3/7 kit, as described in the Materials and methods. A total of 4 populations of cells were distinguished: Live [caspase-3/7(-)/7-AAD(-)], apoptotic [caspase-3/7(+)/7-AAD(-)], apoptotic/dead cells [caspase-3/7(+)/7-AAD(+)], and necrotic [caspase-3/7(-)/7-AAD(+)]. (D) MDA-MB-231 and HS578T cells were treated with 0 or 5 µM ACF for 24 h. Cell death was detected as the percentage of Annexin V and/or 7-AAD-positive cells. The results are expressed as the percentage of surviving cells over control cells. Each value is reported as the mean ± standard deviation and is representative of results obtained from three independent experiments. *P<0.05 compared with non-treated cells. (E) MDA-MB-231 and HS578T cells were treated with 0 or 5 µM ACF for 24 h and then western blot analysis for cleaved PARP expression was performed. β-actin served as the loading control. ACF, acriflavine; 7-AAD, 7-amino-actinomycin D.