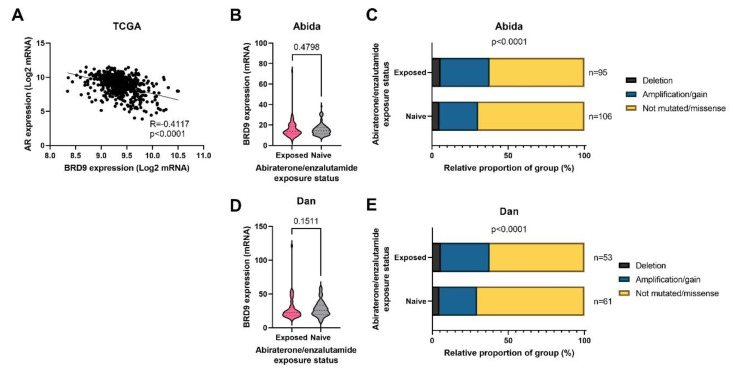
Figure 3.
BRD9 as a potential drug target in CRPC in cancer omics cohorts. (A) Scatterplot with line of best fit showing the correlation between BRD9 and AR expression in the TCGA cohort. Spearman’s R and its associated two-tailed p-value have been calculated. (B) Violin plot showing BRD9 expression in who patients were and were not treated with the second generation antiandrogens abiraterone and enzalutamide in the Abida cohort. p-value was obtained using a Mann Whitney U test. (C) Stacked bar chart showing BRD9 mutation distribution in patients who were and were not treated with the second generation antiandrogens abiraterone and enzalutamide and the number of patients in each sample in the Abida cohort. p-value was obtained using Fisher’s exact test. (D) Violin plot showing BRD9 expression in who patients were and were not treated with the second generation antiandrogens abiraterone and enzalutamide in the Dan cohort. p-value was obtained using a Mann Whitney U test. (E) Stacked bar chart showing BRD9 mutation distribution in patients who were and were not treated with the second generation antiandrogens abiraterone and enzalutamide and the number of patients in each sample in the Dan cohort. p-value was obtained using Fisher’s exact test. Y axis scales on violin plots vary due to experimental variation.