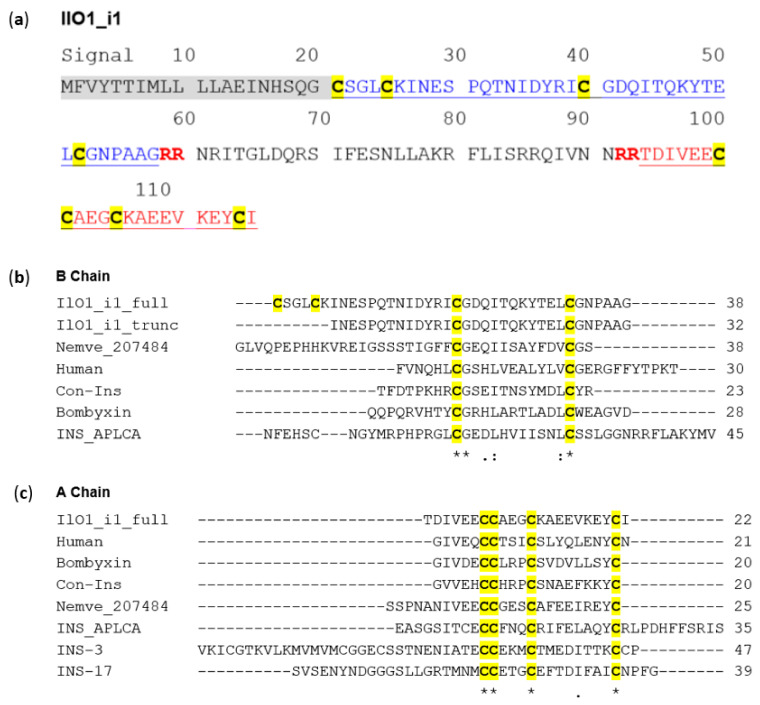
Figure 2.
The full-length sequence of the sea anemone peptide ILP IlO1_i1 and alignment to characterized human and invertebrate insulin-like peptides (ILPs). (a) The full-length amino acid sequence of the sea anemone ILP. Signal peptide highlighted in grey, B-chain in blue, C-chain in black and A-chain in red. (b) Alignment of human and invertebrate B-chains to the predicted full-length B-chain of IlO1_i1 and the truncated sequence used for synthesis. (c) A-chain alignment of IlO1_i1, human and invertebrate ILPs. Sequences used in alignments with UniProt number supplied: Human insulin: P01308 [33]; Con-Ins: Conus geographus: A0A0B5AC95 [14]; Bombyxin: Bombyx mori: Q17192 [8]; Nemve_207484: Nematostella vectensis: A7S6C3 [44]; INS_APLCA: Aplysia californica: Q9NDE7 [10]; INS-3: Caenorhabditis elegans: Q09628 [9]: INS-17: Caenorhabditis elegans: G5EFH1 [9]. Cysteines highlighted in yellow and conserved residues bolded. Sequence alignments performed in Clustal Omega (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/, accessed on May 2020) [27,28,29].