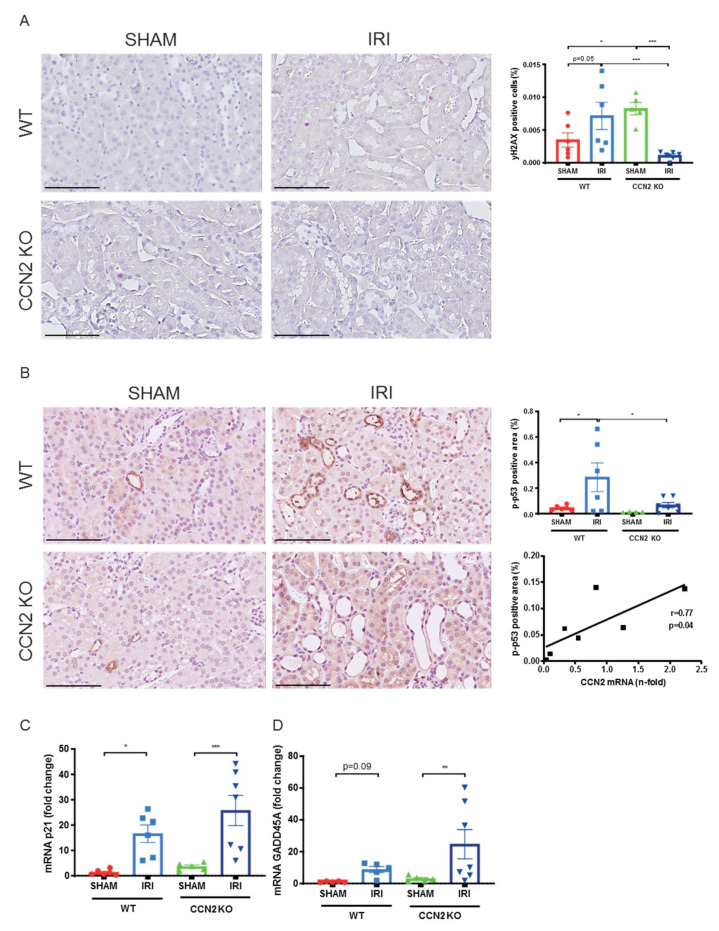
Figure 2.
Near total deletion of CCN2 resulted in reduced DNA damage and p53 activation 4 h after IRI. (A,B) Representative micrographs of mouse renal cortex stained with gamma H2AX (γH2AX; (A) and phosphorylated p53 (p-p53; B). Quantification of γH2AX (A) and p-p53 (B) staining showed that increased DNA damage and p53 activation in IRI kidneys decreased in CCN2 KO mice compared with WT mice. Additionally, p-p53 expression correlated with CCN2 mRNA in CCN2 KO kidneys (B). (C,D) Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) analysis showed that mRNA expression levels of p21CIP1 (p21) and GADD45A increased by IRI in WT and in CCN2 KO kidneys. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n= 6 for WT sham; n = 6 for WT IRI; n = 4–5 for KO sham; n = 6–7 for KO IRI). TBP was used as an internal control. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and, *** p < 0.005. Bar = 100 µm.