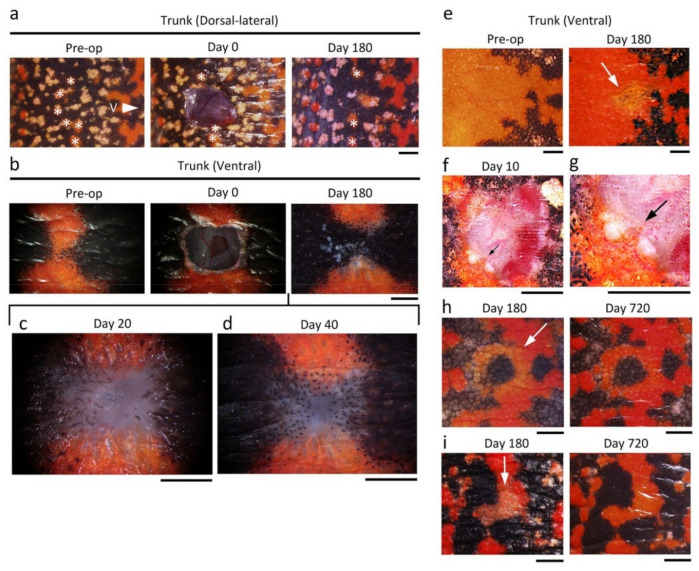
Figure 17.
Restoration of skin color. (a) Sample image of dorsal-lateral skin (patterned area) of the trunk. This area contained a line of small orange spots (asterisks). The skin structure was almost restored by 180 days after operation (Day 180), whereas the orange spots on the excised skin were never restored; instead, the black area expanded into the wound region. V: ventral side. (b–d) Sample images of ventral skin (patterned area) of the trunk. A part of the ventral skin was excised across the black area (Day 0). Melanophores started collective migration from the wound margin (Day 20). This phase corresponds to Stage 5 in which collagen-rich extracellular matrix (reconstructing dermis) has filled the space between the wound epidermis and the wound bed. Collective migration of xanthophores started on Day 40. Melanophores detached from each other by this stage. Skin structure was almost restored by Day 180 whereas melanophores occupied most of the area of the wound region, resulting in an alteration of color pattern. (e) Sample image of ventral skin (plain orange area) of the trunk. A part of the orange area was excised without wounding the black area. Even though the structure of the skin had almost recovered by Day 180, the wound had not blended into its surroundings in terms of color tone (white arrow). (f,g) Sample image showing the collective migration of xanthophores at Day 10. Black arrows: a top of the extending orange area. (h,i) Sample images showing the recovery of the orange color tone in ventral skin. The color tone was monitored for longer than 2 years. The data in (h) was obtained from the animal shown in Figure 1i,j. In these two cases, the orange area created by Day 180 still had a pale tone (white arrow), but by Day 720 it became sufficiently dark to blend into its surroundings. Scale bars: 1 mm.