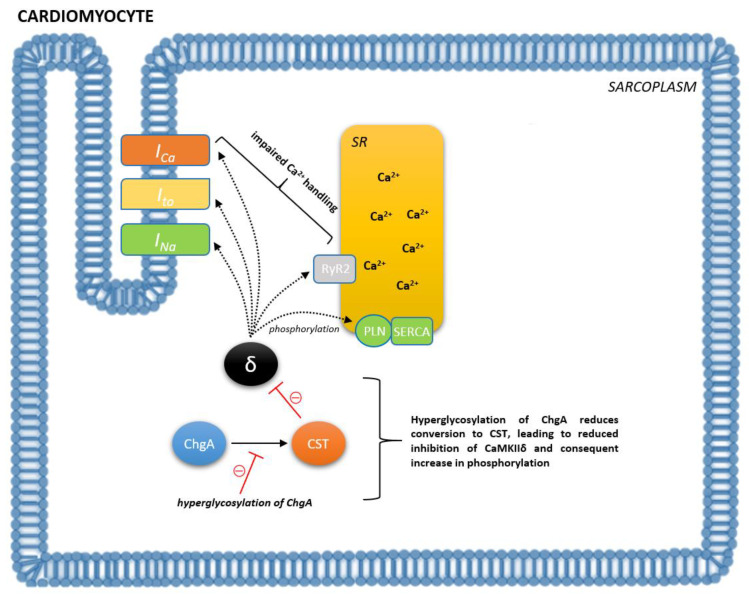
Figure 2.
Putative mechanism by which catestatin contributes to pathophysiology of heart failure (HF). In the setting of HF, hyperglycosylated ChgA cannot be sufficiently cleaved by CST, which leads to reduced inhibition of CaMKIIδ and CaMKIIδ-mediated phosphorylation of cardiac proteins. As a result of increased phosphorylation, calcium handling in cardiomyocytes becomes impaired and dampens cardiac function. Abbreviations: ChgA: chromogranin A; CST: catestatin; CaMKIIδ (δ): the multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II delta; SR: sarcoplasmic reticulum; RYR2: ryanodine receptor 2; SERCA: sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase; PLN: phospholamban.