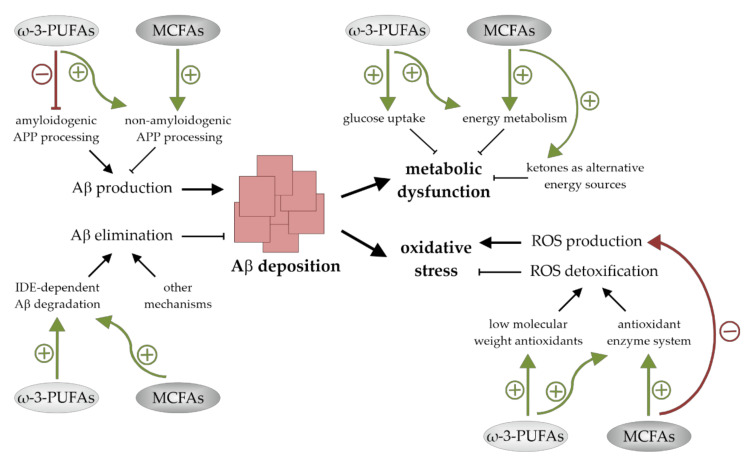
Figure 4.
Summary of the mechanisms by which ω-3-polyunsaturated fatty acids (ω-3-PUFAs) and medium chain fatty acids (MCFAs) reduce cerebral amyloid-β (Aβ) levels, improve brain energy metabolism, and lessen oxidative stress. Both ω-3-PUFAs and MCFAs reduce Aβ deposition by stimulating non-amyloidogenic amyloid precursor protein (APP)-processing and insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE)-dependent Aβ degradation. ω-3-PUFAs additionally suppress Aβ production. Metabolic dysfunction and oxidative stress are also lessened by both fatty acid (FA) classes. Glucose uptake and energy metabolism are increased by ω-3-PUFAs, while oxidative stress levels are reduced in the presence of these FAs due to an increased ROS detoxification. MCFAs improve the cellular metabolic function as well and lower oxidative stress by stimulating reactive oxygen species (ROS) detoxification and reducing ROS generation.