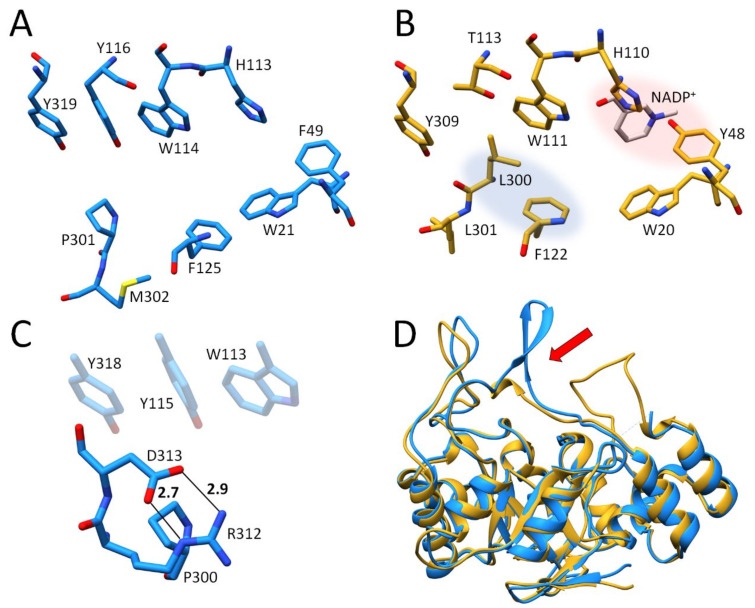
Figure 1.
Comparison of ALR-1 and ALR-2. (A): Active site of ALR-1, EC 1.1.1.2 (1HQT), carbon atoms light blue. (B): Active site of ALR-2 EC 1.1.1.21 (this study), carbon atoms in gold. The anion binding site is highlighted in red and the specificity pocket in blue. (C): Salt bridges between R312 and D313 that would have to be ruptured upon a putative opening of a specificity pocket of ALR-1. (D): Comparison of the flexible C-terminal loops of ALR-1 and ALR-2 (highlighted with a red arrow). Superposition of ALR-1, shown as a golden ribbon, with ALR-2, shown as a blue ribbon. In this and all following figures, carbon atoms are always colored in a way to distinguish and highlight particular structures, whereas oxygen atoms are displayed in red, nitrogen atoms in blue, fluorine atoms in light green, and sulfur atoms in yellow to indicate their atom type.