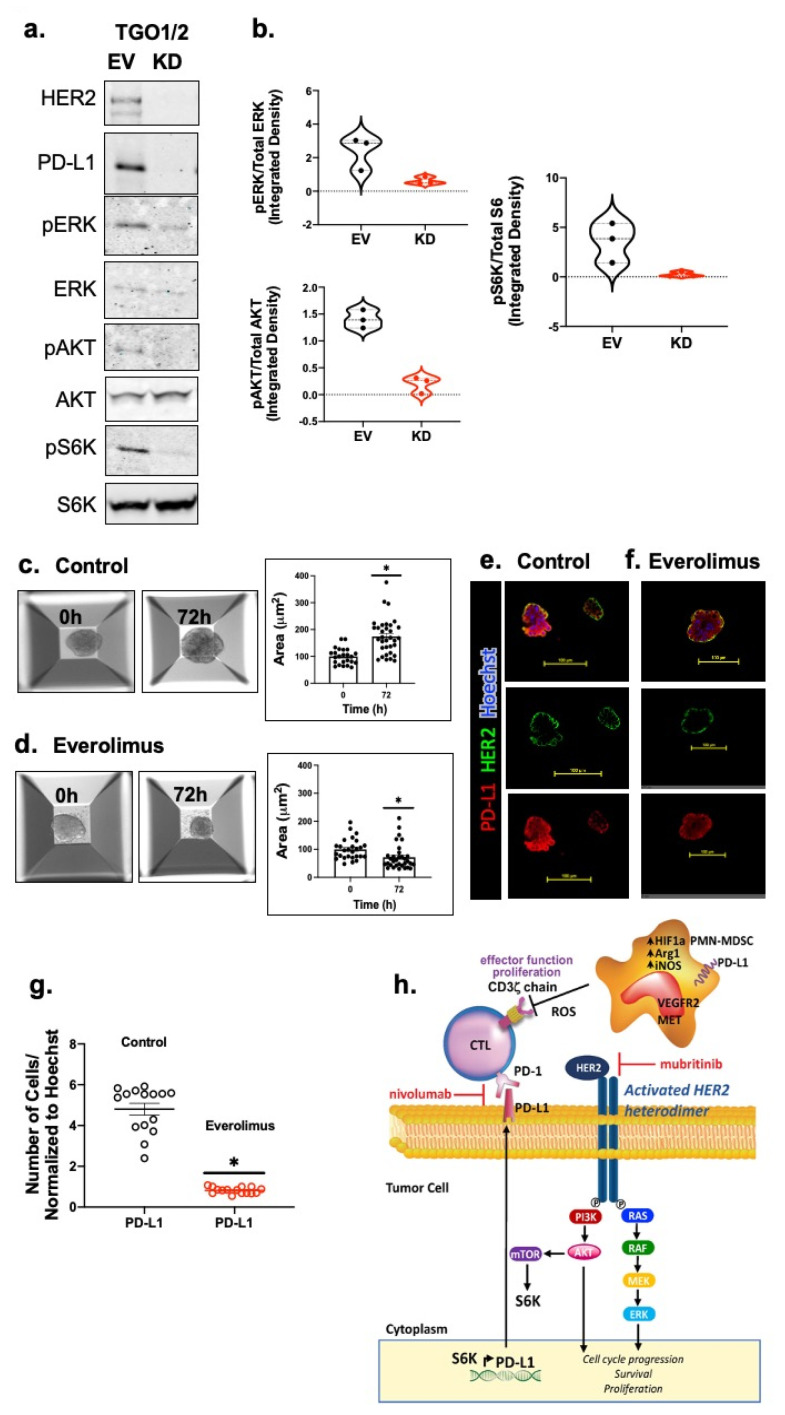
Figure 8.
Inhibition of HER2 regulates PD-L1 expression by suppressing HER2/AKT/MTOR signaling in gastric cancer-derived organoids. The expression of the HER2/AKT/MTOR signaling pathway components were determined by (a) Western blot analysis. (b) Violin plots representing densitometric values of protein bands measured from 8a. Brightfield images and the calculated organoid area in cultures treated with (c) vehicle (control), or (d) Everolimus. n = 15 ROI from 3 different experiments, * p < 0.05 in comparison to vehicle. Immunofluorescences staining using antibodies specific for HER2 (green) and PD-L1 (red) using (e) vehicle (control), or (f) Everolimus treated organoid cultures. (g) Quantification of fluorescence intensity for PD-L1 expression in the control or Everolimus treated cultures. (h) Proposed mechanisms of anti-PD1 inhibition and suppression of MDSCs in a combination immunotherapy strategy for gastric cancer patients. Within the gastric TME, PMN-MDSCs override the checkpoint inhibition by releasing Arg1, iNOS and ROS. Pharmacological inhibition of ERBB2/HER2 could diminish PD-L1 +ve cells from the TME, improving patient responses to immunotherapy. Scale bar = 100 μm.