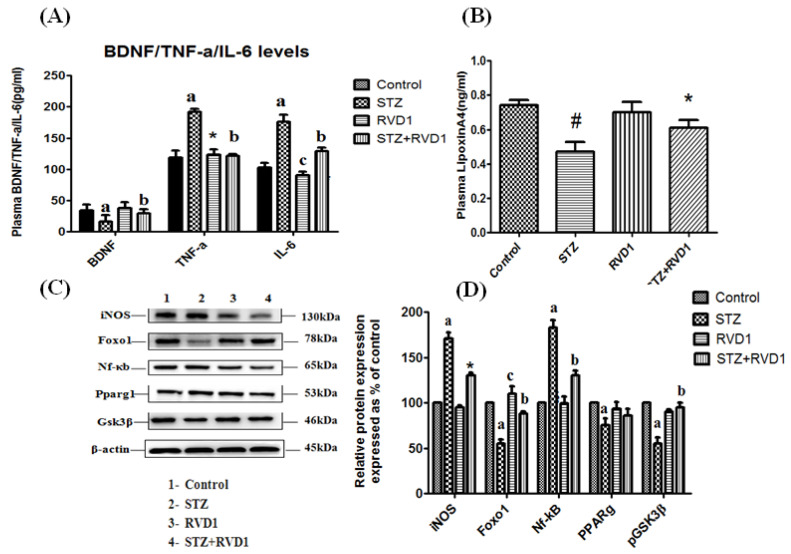
Figure 4.
Effect of RVD1 treatment on plasma levels of BDNF/TNF-α/IL-6/LXA4 and protein expression in pancreatic tissue samples. (A) Plasma BDNF/TNF-α/IL-6 levels in STZ + RVD1- vs. STZ (T1DM)-treated groups estimated at the end of the study (day 30). b p ≤ 0.01 compared to STZ (T1DM), and a p ≤ 0.01 compared to untreated control; TNF-α studies: a p ≤ 0.001; * p ≤ 0.01 compared to control and compared to STZ control; and b p ≤ 0.05 compared to STZ (T1DM); IL-6 studies: a p ≤ 0.01 and c p ≤ 0.05 compared to untreated control and STZ control values. b p ≤ 0.01 compared to STZ (T1DM) group. All values are expressed as mean ± SEM. (B) Measurement of LXA4 levels in the plasma of various groups measured at the end of the study (day 30). # p ≤ 0.001 compared to untreated control. * p ≤ 0.01 compared to STZ (T1DM) control (positive control group). (C,D) Protein expression studies in pancreatic tissue of the rats of various groups. Total protein extracted from the pancreatic tissue samples were collected at the end of the study (day 30) and used for Western blots for Nf-κb, Foxo1, PPAR-γ, p-GSK3β, iNOS, and beta Actin. Equality of loading of the samples was confirmed by beta actin protein expression. All values are expressed as mean ± SEM. a p ≤ 0.01 and c p ≤ 0.05 compared to control values. b p ≤ 0.01 compared to STZ (T1DM) (these data are taken from Reference [15]). It is evident from this data that resolvin D1 not only prevents STZ-induced type 1 DM in experimental animals but also suppresses inflammation, as evidenced by decreased plasma IL-6 and TNF-α levels and decreased expression of NF-kB and iNOS, and an increase in the circulating levels of LXA4 that was suppressed by STZ treatment. Thus, at least, in part, the anti-inflammatory actions of resolvin D1 are mediated by increased formation of LXA4.