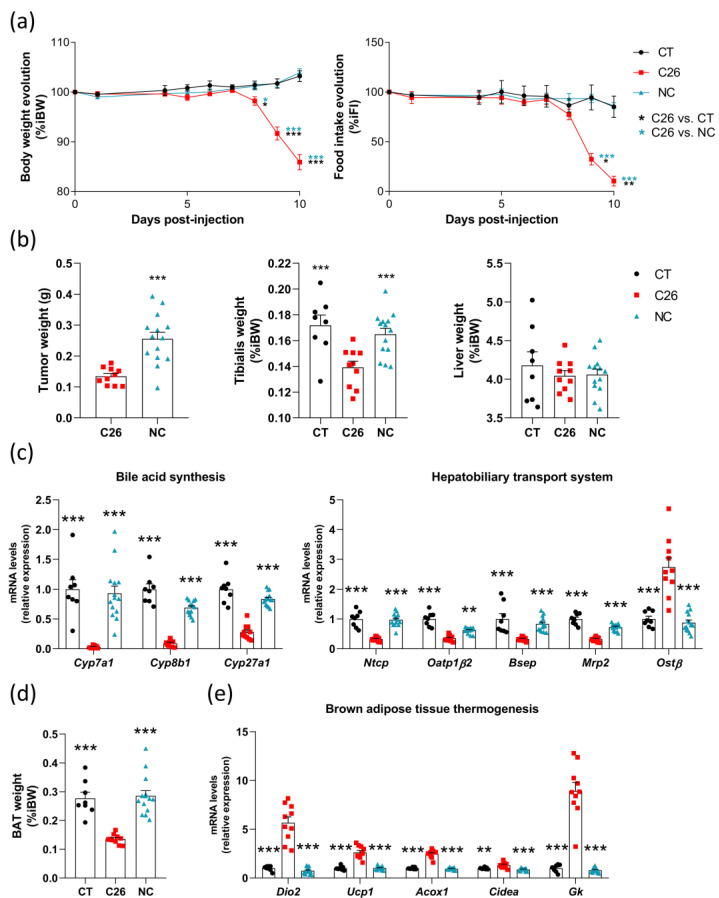
Figure 2.
Many alterations in the liver, muscle, and brown adipose tissue are intrinsically related to cachexia and not to the tumor in C26 mice. (a) Body weight and food intake evolution in sham-injected mice (CT; n = 8), mice injected with cachexia-inducing C26 colon carcinoma cells (C26 mice; n = 10), and mice injected with non-cachexia-inducing C26 colon carcinoma cells (NC mice; n = 14), expressed in % of initial body weight or food intake. (b) Tumor, tibialis, and liver weights of CT, C26, and NC mice. (c) Hepatic mRNA expression levels of genes involved in the bile acid synthesis and the hepatobiliary transport system in CT, C26, and NC mice. (d) The brown adipose tissue weight of CT, C26, and NC mice. (e) mRNA expression levels of genes involved in thermogenesis in the brown adipose tissue of CT, C26, and NC mice. Cyp7a1, cytochrome P450 family 7 sub-family A member 1; Cyp8b1, cytochrome P450 family 8 sub-family B member 1; Cyp27a1, cytochrome P450 family 27 sub-family A member 1; Ntcp, Na(+)/taurocholate transport protein; Oatp1β2, organic anion transporter family member 1B2; Bsep, bile salt export pump; Mrp2, multidrug resistance-associated protein 2; Ostβ, organic solute transporter subunit beta; Dio2, iodothyronine deiodinase 2; Ucp1, uncoupling protein 1; Acox1, acyl-coA oxidase 1; Cidea, cell death-inducing DFFA-like effector A; Gk, glycerol kinase. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. C26.