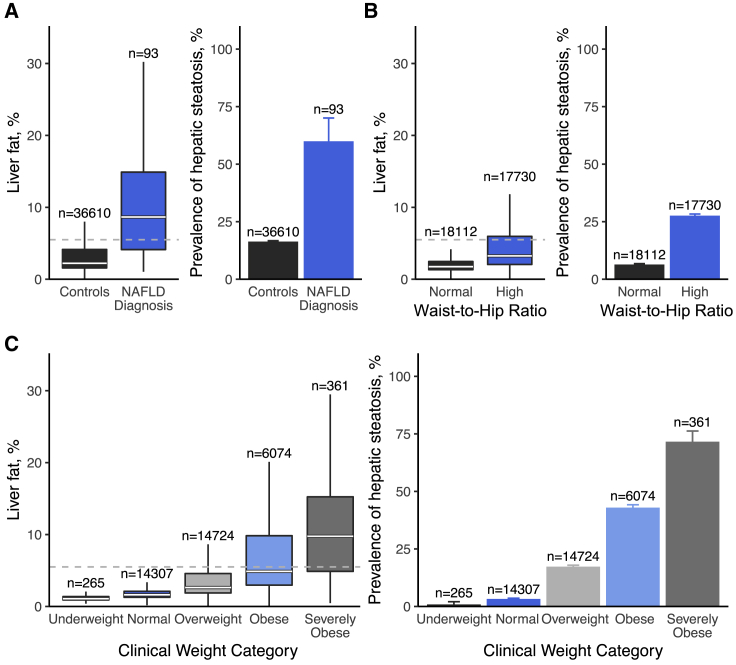
Figure 2.
Associations of clinical parameters with liver fat and hepatic steatosis in 36,703 individuals
(A–C) The distribution of liver fat and prevalence of hepatic steatosis according to the presence of (A) electronic health record diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), (B) high waist-to-hip ratio, and (C) clinical categories of obesity. Hepatic steatosis was defined as liver fat greater than 5.5%.17 High waist-to-hip ratio was defined at time of imaging as greater than 0.9 when male and greater than 0.85 when female.18 Weight categories were defined using BMI at time of imaging:19 underweight, BMI < 18.5 kg/m2; normal, 18.5 ≤ BMI < 25 kg/m2; overweight, 25 ≤ BMI < 30 kg/m2; obese, 30 ≤ BMI < 40 kg/m2; severely obese, BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2. For boxplots, boxes indicate interquartile range (IQR; 25th–75th percentiles), and whiskers indicate distances of 1.5 IQRs from box limits. For bar plots, error bars indicate upper bounds of 95% CI.