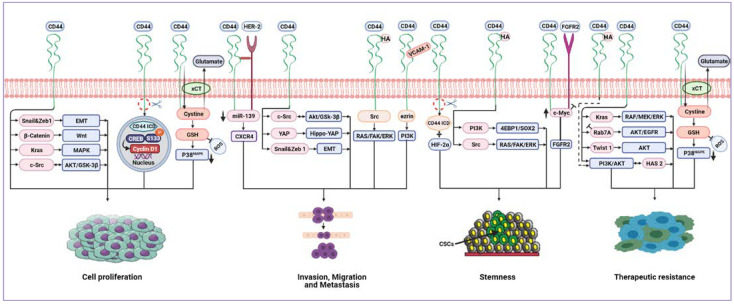
Figure 5.
Cancer-associated signalling pathways modulated by CD44. CD44 can upregulate EMT biomarkers, Snail1 and Zeb1, promoting proliferation and invasion. CD44 activates KRAS through the MAPK pathway, hence promoting tumour cell proliferation and survival. CD44 mediates invasion and metastasis by binding to HER2, leading to the inhibition of miR-139 and upregulation of CXCR4. There is positive crosstalk between CD44 and FGFR2 to maintain cancer stemness. CD44 regulates tumour cell proliferation, invasion and migration by modulating c-Src via AKT/GSK-3β signalling. CD44/VCAM-1 interaction promotes invasion signalling by the ezrin/PI3K pathway. CD44 binds to HA, resulting in stemness development via the PI3K/4EBP1/SOX2 pathway. Also, the HA/CD44 interaction can drive tumour invasion, metastasis and stemness through Src activating RAS/FAK/ERK pathways. Similarly, HA/CD44 stimulates the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway to increase therapeutic resistance. CD44 can sustain EGFR and AKT signalling by inhibition of Rab7A, leading to therapeutic resistance. CD44 promotes the expression of HAS2 by activating the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway. HAS2 further enhances CD44-mediated PI3K/AKT signalling, thus creating a positive feedback loop that drives tumour cell resistance and survival. CD44 can stabilise the cystine/glutamate antiporter (xCT), leading to increased GSH and decreased ROS levels, which, in turn, results in tumour cell proliferation and therapeutic resistance mediated by suppression of the p38 pathway. CD44 regulates tumour cell proliferation by the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. CD44 can promote invasion and migration through the activation of the Hippo-YAP oncogene signalling pathway. CD44 mediates tumour cells resistance by upregulating Twist1 and AKT signalling. CD44-ICD binds to CREB, enhances S133 phosphorylation and enriches CREB recruitment to the cyclin D1 promoter, thus promoting cyclin D1 activity, resulting in cell proliferation. CD44-ICD is released in a hypoxic environment and binds to HIF-2α leading to induced stemness. Abbreviations: EMT, epithelial–mesenchymal transition; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; CXCR4, C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; FGFR2, fibroblast growth factor receptor 2; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; HAS2, hyaluronan synthase 2; GSH, glutathione; ROS, reactive oxygen species; CD44-ICD, CD44 intracellular domain; CREB, cAMP response element-binding; HIF-2α, hypoxia-inducible factors 2 alpha.