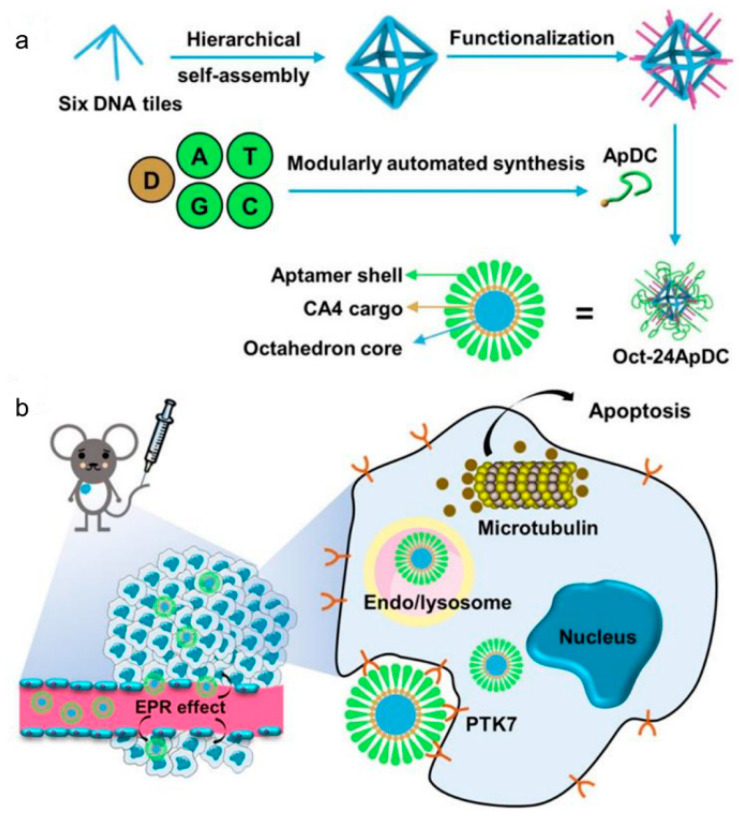
Figure 5.
Schematic illustration of targeted delivery of CA4-FS by DNA octahedron wireframe. (a) Six DNA tiles are layered and self-assembled to form an octahedral framework; after the nucleic acid aptamer is functionalized, single-chain handles connected on each side of the framework can be combined with a synthesized CA4-FS module; and with designing a sequence of the single-chain handles, different numbers of CA4-FS can be connected. The DNA nanocarrier in core-shell mode is finally formed, which is called CA4-Oct, reproduced with permission from Reference [79], Copyright 2020 American Chemical Society; (b) structural advantages: The outer three-dimensional spatial distribution of multivalent Sgc8c aptamers allows more precise binding to the tumor marker PTK7 receptor; enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) of passive targets improves delivery efficiency, reducing direct exposure of CA4 to avoid premature biotoxicity; the dense DNA octahedral framework facilitates the insertion of flexible CA4-FS into solid tumors to release the drug, reproduced with permission from Reference [79], Copyright 2020 American Chemical Society.