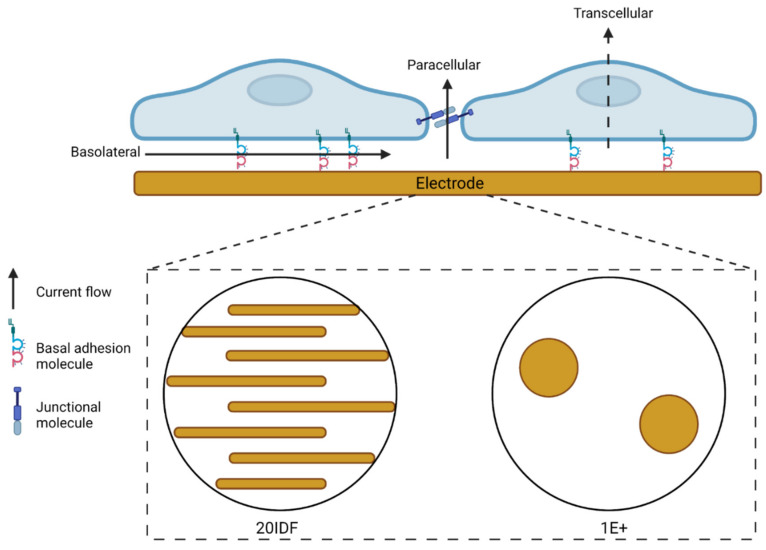
Figure 1.
Electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS) schematic of current flow. Resistance measurements acquired by ECIS are a consequence of current flow through multiple pathways. Current flows through the basolateral, paracellular, and transcellular compartments. The cellular biology dictates the pathway that provides the most resistance to current flow. Current flow is impeded by the presence of strong basal adhesion proteins, paracellular junctional proteins and the cell body atop the electrode. ECIS electrode configurations include, but are not limited to, an interdigitated orientation of electrodes that measure a large surface area of a well, or two small circular electrodes that measure a comparatively smaller surface area of a well. Consult the Applied Biophysics website (https://www.biophysics.com/; accessed on 19 October 2021) for the most up-to-date array types and configurations.