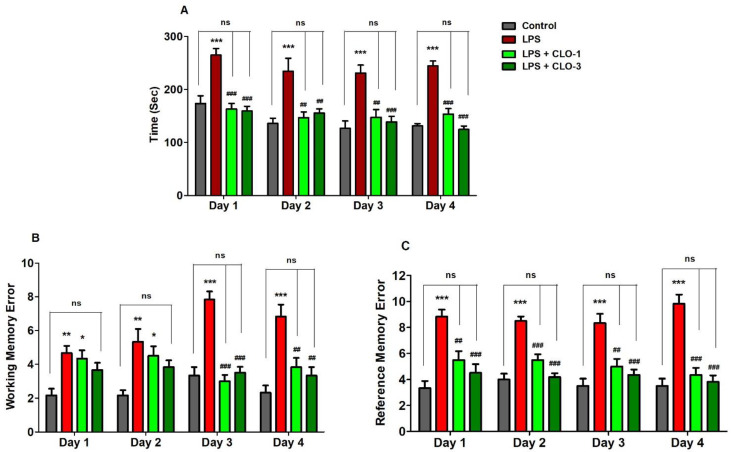
Figure 2.
Effect of the clobenpropit (CLO) on the (A) time taken to consume all five baits (TTB), (B) working memory error (WME), and (C) reference memory error (RME) on day 1 to day 4 of memory assessment in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced mice using radial arm maze. LPS-CLO-1 and LPS-CLO-3 refer to administration of clobenpropit (1 or 3 mg/kg, p.o., respectively) and lipopolysaccharides (250 μg/kg, i.p.). TTB, WME and REM were increased by LPS-induced neuroinflammation. However, CLO treatment significantly reduced the LPS-induced TTB, WME and REM increments. The results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 6). One-way ANOVA (TTB; F(3,20) = 17.87, p < 0.001 for day 1; F(3,20) = 9.030, p < 0.001 for day 2; F(3,20) = 11.74, p < 0.001 for day 3; and F(3,20) = 25.95, p < 0.001 for day 4), (WME; F(3,20) = 6.460, p < 0.01 for day 1; F(3,20) = 6.272, p < 0.01 for day 2; F(3,20) = 28.97, p < 0.001 for day 3; and F(3,20) = 12.39, p < 0.001 for day 4) (REM; F(3,20) = 14.88, p < 0.001 for day 1; F(3,20) = 29.21, p < 0.001 for day 2; F(3,20) = 13.41, p < 0.001 for day 3; and F(3,20) = 26.52, p < 0.001 for day 4) was followed by Tukey–Kramer multiple comparisons tests.* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001 as compared to the control group; ns, not significant as compared to the control group; ## p < 0.01 and ### p < 0.001 as compared to the LPS-treated group.