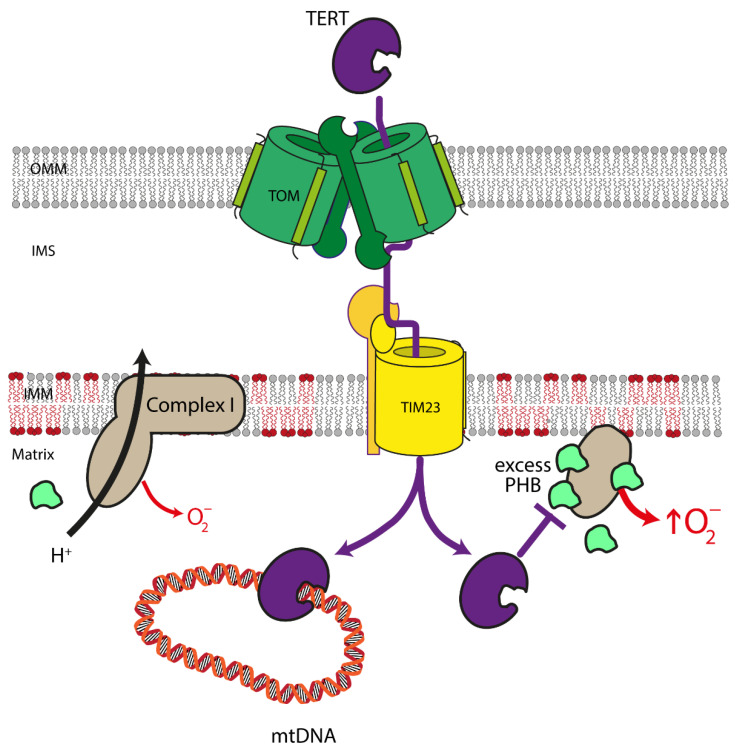
Figure 4.
Mitochondrial functions of TERT in the cardiovascular system. In the mitochondria, Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (TERT) binds to mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and protects it against damage. In addition, mitochondrial TERT improves the stoichiometry of the different subunits of complex I of the electron transport chain. Moreover, an increase in mitochondrial TERT reduces the levels of Prohibitin (PHB) in these organelles, which—when in excess—stabilizes free matrix arm subunits of complex I of the electron transport chain resulting in increased production of mitochondrial superoxide. Consequently, mitochondrial TERT improves complex I composition and activity, decreases mitochondrial reactive oxygen levels, and, thereby, contributes to enhanced mitochondrial functionality.