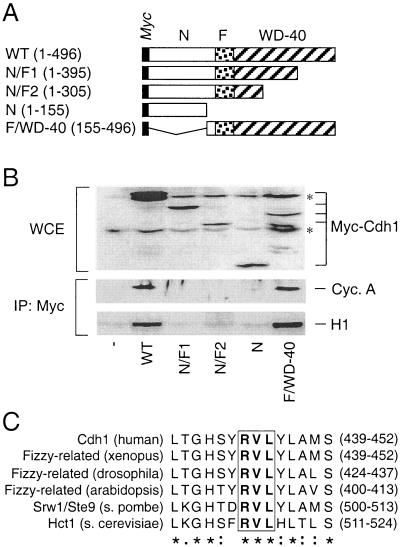
FIG. 2.
Cdh1 interaction with cyclin A is mediated by the C-terminal WD-40 repeat domain containing a conserved cyclin-binding motif. (A) Schematic representation of the myc-tagged Cdh1 truncation mutants. WT, wild type; N, N terminus; F, Fizzy domain; WD-40, the C-terminal domain containing multiple WD-40 repeats (the numbers in parentheses indicate the ranges of amino acids). (B) U-2-OS cells were transiently transfected with expression plasmids coding for the indicated myc-tagged deletion mutants. Control cells (−) were transfected with the empty pXmyc plasmid. Expression of the deletion mutants was verified by Western blotting the whole-cell extracts (WCE) prepared from the transfected cells (asterisks, nonspecific bands). Thirty-six hours after transfection, the cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with an antimyc antibody, and the purified immunocomplexes were either analyzed by Western blotting to detect associated cyclin A or subjected to an in vitro kinase assay with histone H1 as a substrate. (C) Identification of the cyclin-binding domain within the Cdh1 WD-40 repeat domain in diverse organisms. The degree of amino acid conservancy within the selected region is indicated; the core RVL sequence is boxed and in boldface. Identical (asterisks), conserved (colons), and semiconserved (dots) amino acids are indicated.