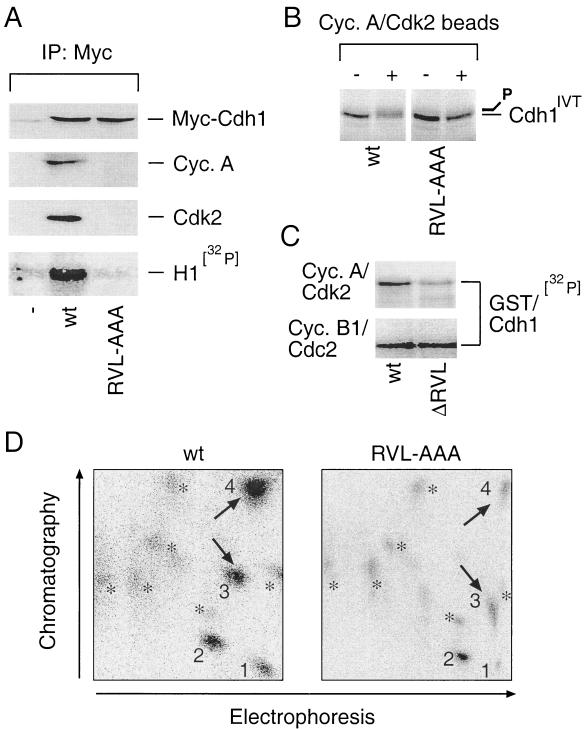
FIG. 3.
Integrity of the cyclin-binding domain is required for Cdh1 recognition and phosphorylation by cyclin A-Cdk2. (A) U-2-OS cells were transfected with the pXmyc expression plasmids containing either no insert (−) or the wild-type (wt) and the cyclin binding-deficient (RVL-AAA) forms of Cdh1. After 36 h cells were lysed and the myc immunocomplexes were analyzed for the presence of myc-Cdh1, cyclin A, and Cdk2 with the indicated antibodies and for associated histone H1-kinase activity as described for Fig. 2B. IP, immunoprecipitation. (B) Wild-type or RVL-AAA forms of Cdh1 translated in vitro were used as substrates in an in vitro kinase reaction mixture supplemented by Sepharose beads with active cyclin A-Cdk2 complexes immunopurified from U-2-OS cell extract (+). Beads coated with nonimmune rabbit immunoglobulin were preincubated in lysates from U-2-OS cells and added into the control reactions as indicated (−). Productive phosphorylation of wild-type (but not RVL-AAA) Cdh1 is manifested as a smear and retarded mobility after the kinase reaction was resolved by SDS-PAGE. (C) An in vitro kinase reaction with immunoprecipitated cyclin A-Cdk2 and cyclin B1-Cdc2 was performed essentially as for panel C except that the bacterially purified GST-tagged wild-type and ΔRVL forms of Cdh1 were used as substrates and the reaction mixture was supplemented with [γ-32P]ATP (ΔRVL indicates that the RVL amino acids representing the core of the Cdh1 cyclin-binding domain were deleted). (D) Tryptic phosphopeptide maps of 32P-labeled wild-type (wt) and cyclin binding-deficient (RVL-AAA) myc-tagged Cdh1 proteins transiently expressed in U-2-OS cells and immunoprecipitated with 9E10 antibody. 1 to 4, prominent, strongly labeled phosphopeptides; asterisks, weakly labeled spots; arrows, phosphopeptides most sensitive to cyclin-binding motif disruption.