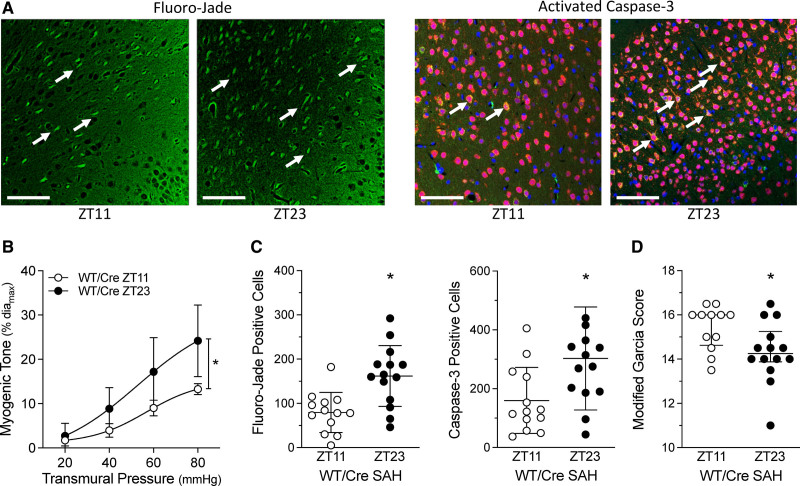
Figure 2.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)–induced injury associates with cerebral artery myogenic tone. SAH was induced in tamoxifen-treated, Cre-expressing control mice (Cre-expressing wild-type control [tamoxifen treated; WT/Cre]) at Zeitgeber time 11 (ZT11) or Zeitgeber time 23 (ZT23); behavioral assessments and tissue collection were conducted 48 h afterwards. A, Representative images of cortical cells stained with Fluoro-Jade (left) and for activated caspase-3 expression (right); arrows point to positively stained cells (Bar=60 µm). B–D, Show the association between myogenic tone at the time of SAH and the resulting injury that ensues. B, Before the SAH surgery, olfactory cerebral artery myogenic tone is higher at ZT23, relative to ZT11 (n=5). C, Positive cell counts for Fluoro-Jade staining and activated caspase-3 are higher when SAH is induced at ZT23, relative to ZT11 (n=13–14). D, Modified Garcia scores are lower when SAH is induced at ZT23, relative to ZT11. Modified Garcia scores in D are presented as medians±interquartile range and compared with a Mann-Whitney test. *P<0.05.