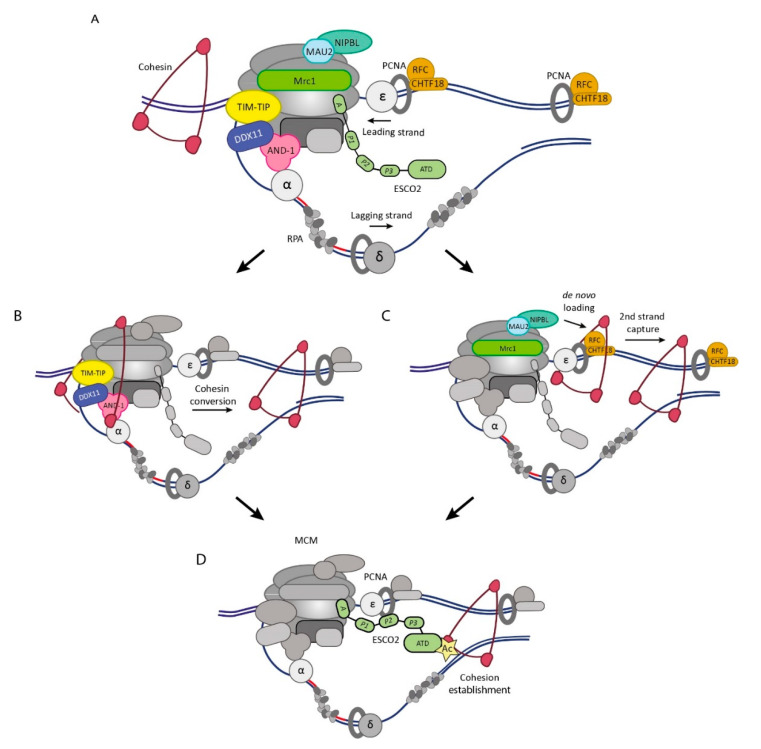
Figure 2.
Entrapment of sister chromatids during DNA replication: (A) Upon separation of the two parental DNA strands by the CMG, the DNA polymerases δ and ε synthesize DNA assisted by PCNA. Cohesion establishment factors are indicated in color. (B) The conversion pathway consists of TIMELESS-TIPIN, DDX11, and AND-1, which facilitate the transfer of pre-loaded cohesin rings to tether the two sister chromatids behind the fork, in a lagging strand oriented process. (C) The de novo pathway, consisting of the PCNA loader CHTF18-RFC, Mrc1 (established in yeast) and NIPBL-MAU2, may involve initial capture of the leading strand, followed by lagging strand capture while it is still single stranded. (D) ESCO2 acetylates SMC3 to establish cohesion. ESCO2 interacts with the replisome through PCNA interacting domains (depicted as P1–P3) and the MCM-interacting Box A domain (A). ATD, acetyltransferase domain. For further details, see text.