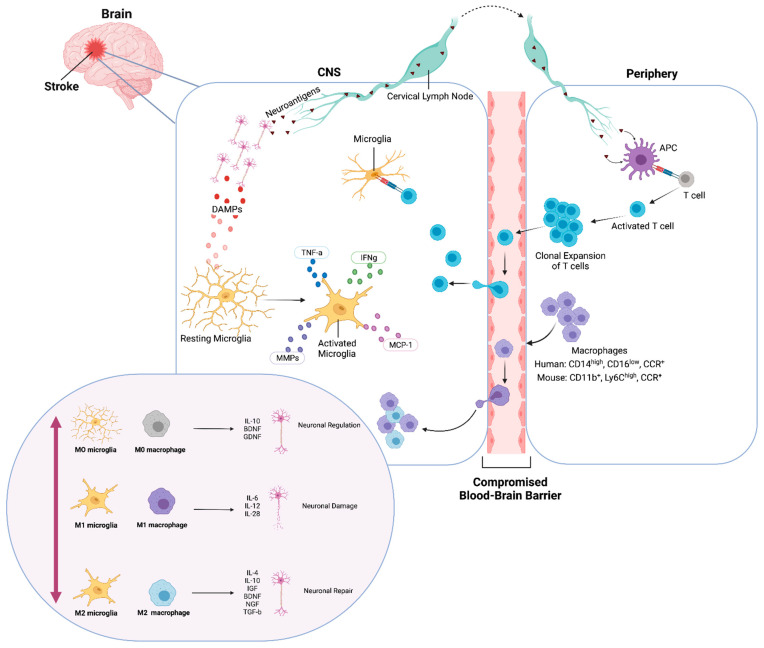
Figure 1.
Ischemic inflammatory response of microglia and macrophages. Immediately after an ischemic event, DAMPs activate resting (M0) microglia and neuroantigens are released. Microglia produce cytokines and chemokines. Transendothelial migration of monocytes and macrophages occurs through the compromised BBB. Neuroantigens are processed and presented by APCs and activate CD4+ T-cells, which undergo clonal expansion, promoting inflammation and neuronal damage. Classically activated (M1) microglia and macrophages release pro-inflammatory factors and contribute to neuronal damage. Conversely, alternatively activated (M2) microglia and macrophages release anti-inflammatory factors and contribute to neuronal repair and neurogenesis. Created with BioRender.com.