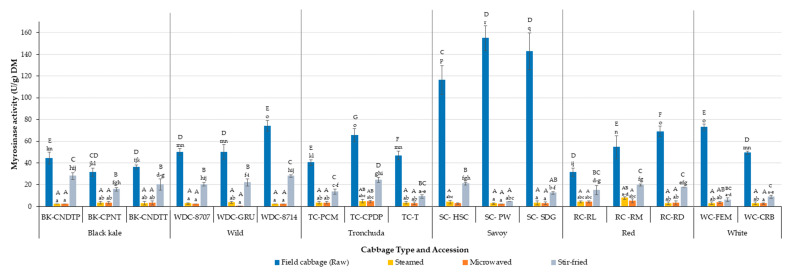
Figure 1.
Comparison of the myrosinase activity of raw versus cooked cabbage morphotypes and accessions (U/g DW). Values are means of three biological (raw samples) or processing (cooked samples) replicates (each replicate comprising 4–5 cabbage heads) and two technical replicates (n = 6). Error bars represent standard deviation from mean values. Letters “A–G”: bars not sharing a common uppercase letter differ significantly (p < 0.0001) between accessions and treatments within a cabbage morphotype. Letters “a–r”: bars not sharing a common lowercase letter differ significantly (p < 0.0001) between cabbage morphotypes, accessions, and treatments. Key: BK-CNDTP: cavolo nero di toscana o senza palla; BK-CPNT: cavolo palmizio; BK-CNDTT: cavolo nero di toscana o senza testa; WD-8707: wild cabbage 8707; WD-GRU: wild cabbage 7338; WD-8714: wild cabbage 8714; TC-PCM: penca mistura; TC-CPDP: penca povoa; TC-T: tronchuda; SC-HSC: hybrid savoy wirosa; SC-PW: pointed winter; SC-SDG: dark green; RC-RL: red langendijker; RC-RM: rocco marner (hybrid); RC-RD: red Danish; WC-FEM: early market; WC-CRB: couve repolho.