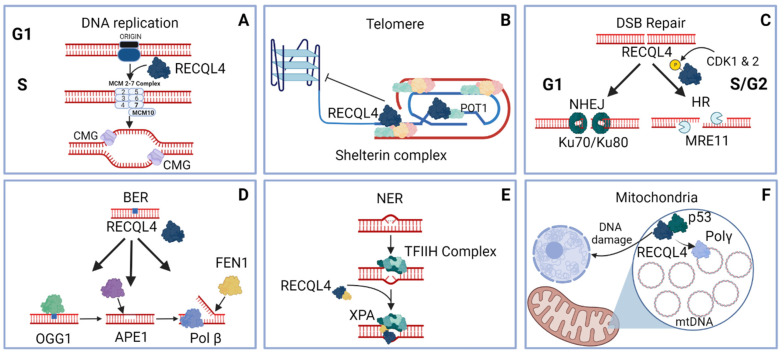
Figure 3.
RECQL4 roles in genome maintenance. (A) RECQL4 (dark blue) is critical for replication initiation, RECQL4 is loaded following the pre-RC to mediate loading of DNA polymerase α and the CMG complex (light purple). The origin is indicated by a black and dark blue boxes and the MCM complex, consisting of MCM2-7, is shown with light blue boxes and MCM10 in a light blue box as well. (B). RECQL4 interacts with the Shelterin complex [POT1-TRF1-TRF2 (teal-beige-pink proteins, respectively)] to resolve D-loops (blue and red DNA structure on right) and G-quadruplexes (light blue structured DNA on left). (C). RECQL4 participates in DSB repair in a cell cycle dependent manner. RECQL4 functions with the KU complex (green circle) during G1 to mediate DNA end joining (NHEJ). During S/G2, RECQL4 cooperates with MRE11 (light blue pacman) to promote DNA end resection during homologous recombination (HR). (D). RECQL4 stimulates the function of multiple BER proteins at different stages. At the initial stage of damage recognition, RECQL4 stimulates OGG1 (light green protein) lyase activity, subsequently RECQL4 stimulates APE1 (purple protein) endonuclease activity, and finally RECQL4 stimulates FEN1 (yellow protein) incision and Pol β (light blue protein) DNA synthesis activities. (E). RECQL4 mediates repair of UV lesions through its interaction with XPA (yellow). XPA works to verify the damage following damage recognition and DNA unwinding by the TFIIH complex (complex of teal proteins). (F). RECQL4 interacts with p53 (green protein) to mediate mtDNA synthesis through Polγ (light blue) and to sequester p53 in the mitochondria. However, following DNA damage, the interaction between RECQL4 and p53 is lost and both proteins relocalize to the nucleus to mediate the DNA damage response. Created using biorender.com, accessed on 11 November 2021.