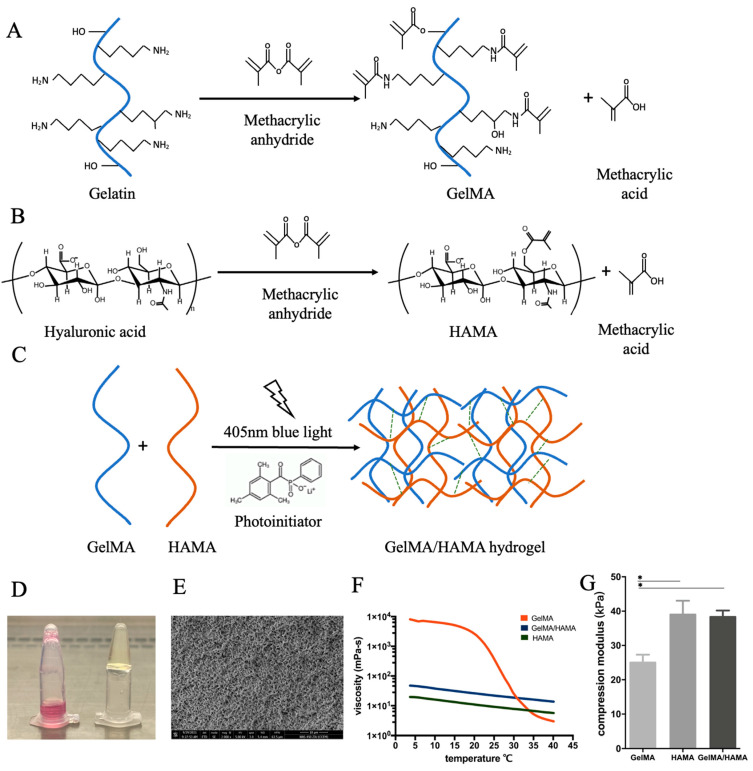
Figure 1.
Assembly of the hydrogel construct from GelMA and HAMA polymer chains. Prior to gel assembly, gelatin and hyaluronic acid are methacrylated separately and lyophilized for storage. (A) The binding of methacrylate groups to the primary NH2 groups of gelatin. (B) The binding of methacrylate groups to the hydroxyl groups of hyaluronic acid. (C) To create a hybrid hydrogel, a solution of methacrylated gelatin and methacrylated hyaluronic acid was formed by rehydrating lyophilized powders of both, then crosslinked by the addition of a photoinitiator (LAP) and 405 nm blue light irradiation for 30 s. (D) GelMA/HAMA hydrogel solution before (left) and after (right) 30 s of blue light treatment. (E) SEM of the cross-section of the GelMA/HAMA hydrogel (scale bar: 10 µm). (F) Rheological properties of the 12.5% GelMA, 2% HAMA, and 8% GelMA/0.8% HAMA hydrogels. Viscosity of three different solutions as a function of temperature was measured at a shear rate of 100 s−1. (G) Young’s modulus of the 12.5% GelMA, 2% HAMA, and 8% GelMA/ 0.8% HAMA hydrogel constructs (* p < 0.05).