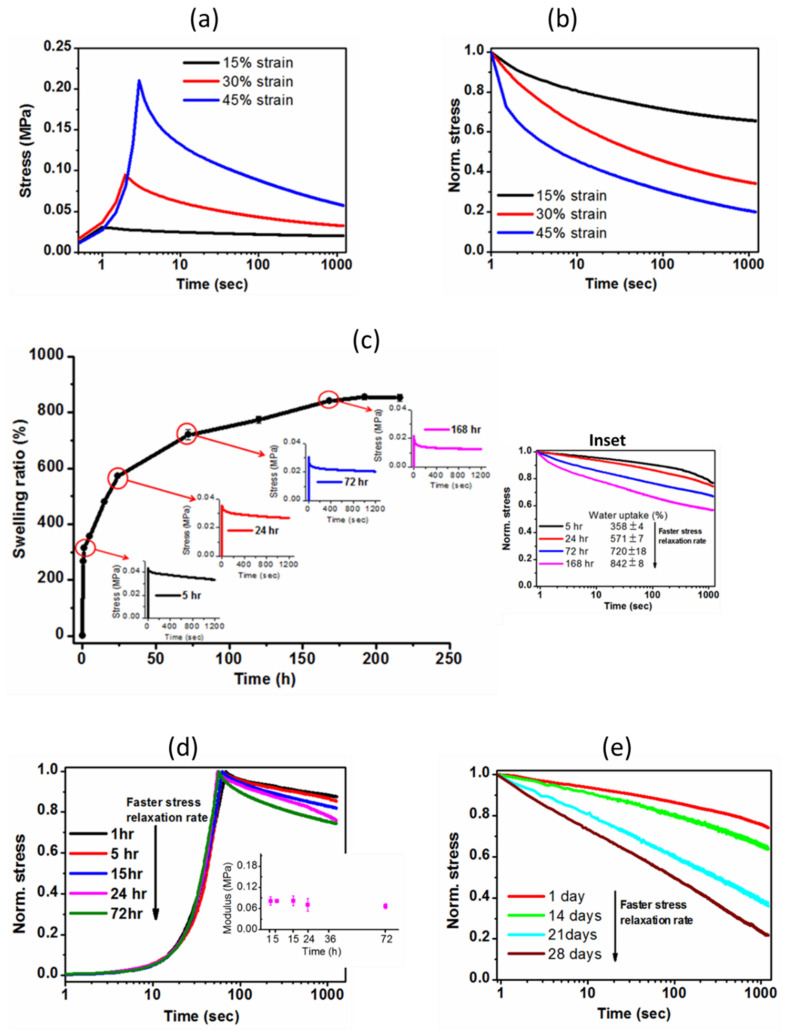
Figure 8.
(a) Decaying of stress over time at different deformation levels (15, 30 and 45% strain) and (b) corresponding relative rate of stress relaxation; (c) Swelling ratio was calculated at different time intervals of immersion in distilled water at 37 °C. Stress relaxation curves of the hydrogel at a strain of 15% subjected to compression testing at four points (5, 24, 72 and 168 h) as swelling increased to equilibrium (inset shows the comparison of stress relaxation behaviors). Stress was normalized by the initial (max.) stress; (d) Stress relaxation profile of hydrogel held at 15% strain at different immersion time intervals up to 3 days (inset shows the initial elastic moduli of hydrogel at 1, 5, 15, 24 and 72 h). Elastic moduli are nearly constant, but water uptake (%) increases from 314 ± 5% (at 1 h) to 720 ± 18% (at 72 h); (e) Stress relaxation of the hydrogel at 1, 14, 21 and 28 days of hydrolytic degradation at 37 °C.