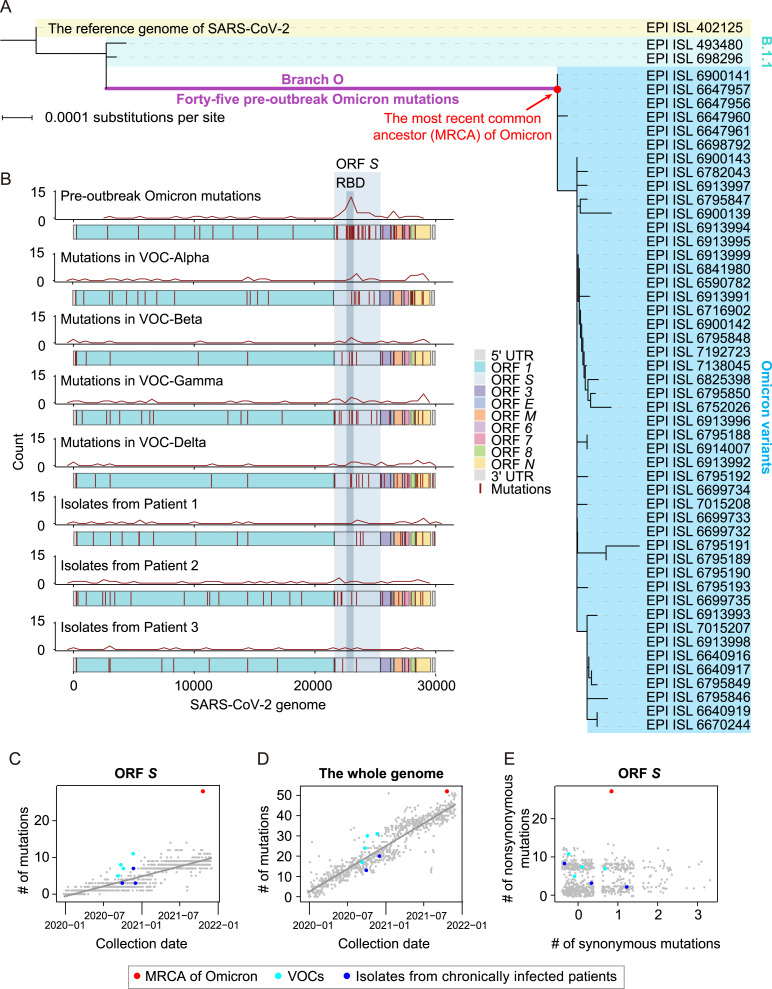
Fig. 1.
The characterization of pre-outbreak Omicron mutations. A: The phylogenetic tree of Omicron variants, including the reference genome of SARS-CoV-2, two B.1.1 variants, and 48 Omicron variants. A total of 45 pre-outbreak Omicron point mutations in the long branch (Branch O, labeled in purple) leading to the MRCA of Omicron (dot in red) in the phylogenetic tree are shown in Fig. S1. B: The genomic distribution of the 45 pre-outbreak Omicron mutations, the mutations detected in each progenitor of the other four VOCs (i.e., Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta), and the mutations identified from the SARS-CoV-2 isolates of three chronically infected patients. The density curves for mutations were generated by the geom_freqpoly function in R. C: Number of mutations that accumulated in ORF S of the MRCA of Omicron (red), the other four VOCs (cyan), and three SARS-CoV-2 isolates from chronically infected patients (blue), against the date of sample collection. SARS-CoV-2 variants randomly sampled (one variant per day) are shown in grey, and the grey line represents their linear regression. D: Similar to (C), for the whole genome. The dot for a variant isolated from a chronically infected patient is overlapped with a VOC. E: A scatterplot shows the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous mutations in ORF S (jittered in order to reduce overplotting). UTR, untranslated region; RBD, receptor-binding domain.