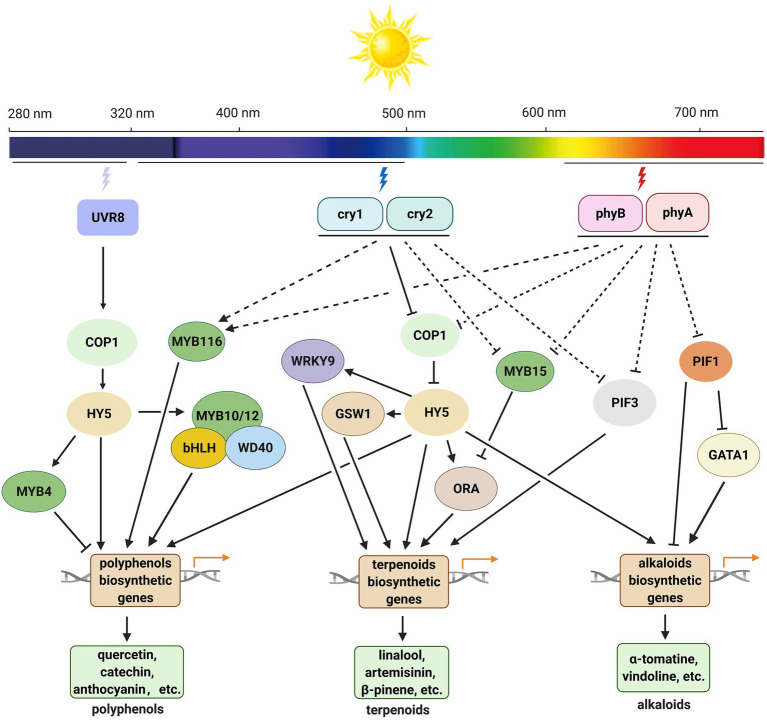
Figure 4.
Working model for light-mediated biosynthesis of polyphenols, terpenoids, and alkaloids in medicinal plants. Upon UV-B radiation, the UVR8 homodimer undergoes monomerization and interacts with COP1, which increases COP1 stability and induces HY5 expression. HY5 regulates the expression of genes encoding transcription factors and/or key enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of SMs and affects the accumulation of SMs under UV-B. Under blue and red light, cryptochromes (cry1 and cry 2) and phytochromes (phyA and phyB) inhibit the E3 ligase activity of COP1, HY5 accumulates in nucleus and promotes the expression of transcription factor and/or key enzyme genes in the related biosynthetic pathways of SMs. Phytochromes may also affect the accumulation of alkaloids by mediating the function of PIF1 and PIF3 in some species. COP1, CONSTITUTIVELY PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1; cry1 and cry2, cryptochrome 1 and cryptochrome 2; GATA1, GATA-type transcription factor 1; GSW1, GLANDULAR TRICHOME-SPECIFIC WRKY 1; HY5, LONG HYPOCOTYL 5; ORA, AP2/ERF type transcription factor; phyA and phyB, phytochrome A and phytochrome B; PIF1, phytochrome interacting factor 1; PIF3, phytochrome interacting factor 3; UVR8, UV RESISTANCE LOCUS 8.