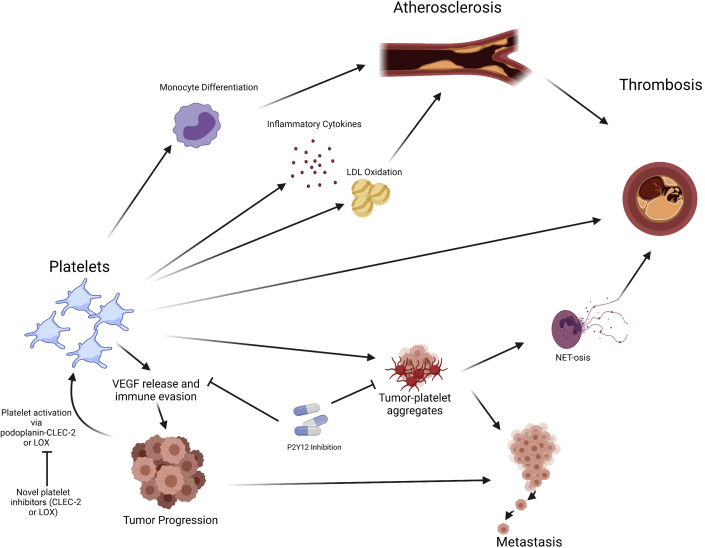
Figure 2.
Platelets Are Involved in the Progression of Atherosclerosis and Cancer
Arrows indicate relationships: platelets facilitate progression of atherosclerosis through monocyte differentiation, release of inflammatory cytokines and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation. Additionally, platelets contribute to cancer progression and metastasis through release of proangiogenic factors, immune evasion, and hematogenous spread via tumor-platelet aggregates. P2Y12 inhibition may attenuate platelet-facilitated tumor progression. CLEC-2 = C-type lectin-like type II transmembrane receptor; LOX = lysyl oxidase; NET = neutrophil extracellular trap.