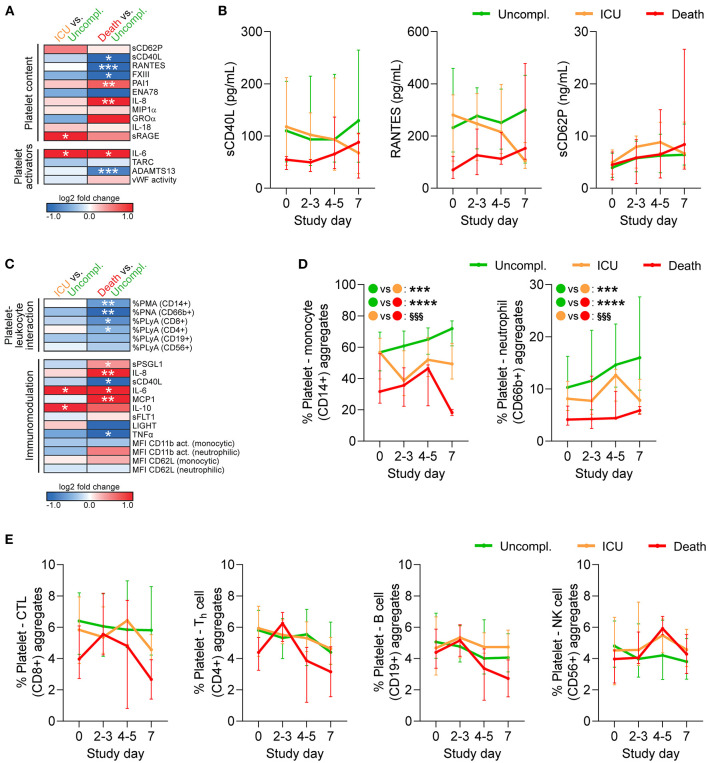
Figure 4.
Reduced platelet-derived plasma factors and platelet-leukocyte interaction in COVID-19 patients with fatal outcome. Whole blood (n = 97 patients) and plasma (n = 106 patients) was analyzed by flow cytometry, multiplex analysis and ELISA (A,B) for platelet-contained and platelet-activating mediators and (C-E) for platelet-leukocyte aggregates (PLA) and markers of platelet-mediated immunomodulation. (A,C) Heatmap visualization of expression profiles at study day 0 in patients requiring ICU treatment or with fatal outcome relative to patients with uncomplicated disease. Data are represented as log2-fold change relative to uncomplicated disease. (B) Plasma levels of soluble CD40L (sCD40L), regulated upon activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted (RANTES/CCL5) and sCD62P were monitored over 1 week after study entry. (D,E) Percentages of PLA in whole blood were monitored over 1 week after study entry. (D) PLA formation with CD14+ monocytes and CD66b+ neutrophils. Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences to uncomplicated, section signs (§) indicate significant differences between ICU and death. (E) PLA formation with CD56+ natural killer (NK) cells, CD19+ B cells, CD8+ cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTL) or CD4+ T-helper (Th) cells. n = 106 (plasma content) or 97 (cell analysis) patients. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; PMA, platelet-monocyte aggregates; PNA, platelet-neutrophil aggregates; PLyA, platelet-lymphocyte aggregates. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001; §§§p < 0.001.