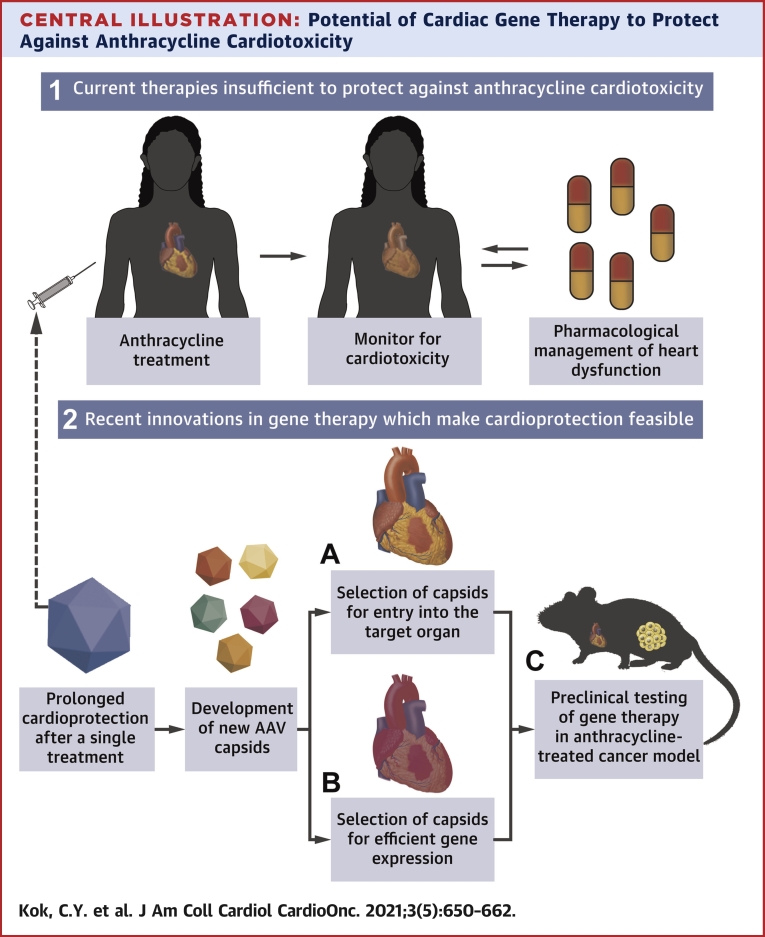
Central Illustration.
Potential of Cardiac Gene Therapy to Protect Against Anthracycline Cardiotoxicity
(1) Current therapies do not provide sufficient protection against anthracyclines, and require monitoring of heart function and subsequent intervention throughout chemotherapy. (2) Adeno-associated virus (AAV) mediated gene therapy may provide a way to confer long-term cardioprotection after a single treatment, by targeted delivery of therapeutics to the heart. This can be achieved by development of new capsids with the enhanced ability for (A) cell entry and (B) gene expression in the target cells. (C) Application of the therapeutic vector can then be tested in clinically relevant small animal models to assess cardioprotection and cancer cytotoxicity.