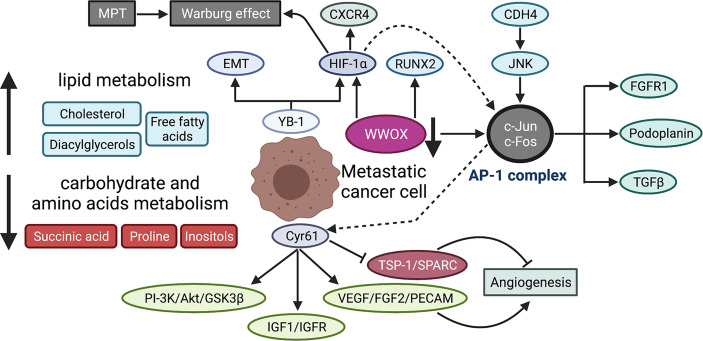
Figure 4.
Metabolic reprogramming during OS metastasis. MPT promotes Warburg effect in OS cells by suppressing mitochondrial function. The serum metabolic profile of lung metastasis shows lowered carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism but an elevated lipid metabolism. YB-1 contributes to metastasis by translational activation of EMT and HIF-1α, which then induces CXCR4 expression. Cyr61 enhances the metastatic potential of OS cells through multiple signaling pathways, including PI-3K/Akt/GSK3β, IGF1/IGFR, and angiogenesis-associated signaling (increased VEGF, FGF2, PECAM and reduced TSP-1, SPARC). WWOX maintains mitochondrial respiration and inhibits Warburg effect by physical interaction with HIF-1α. WWOX also suppresses c-Jun activity by physical association while CDH4 overexpression activates c-Jun via the JNK pathway. AP-1 is a transcriptional complex, mainly composed of c-Jun and c-Fos, which promotes metastatic potential by upregulating several downstream effectors, including FGFR1, podoplanin, and TGFβ. The dotted lines indicate the mechanistic study is performed in melanoma cells, that is, HIF-1α interacts with AP-1, which then binds to AP-1-binding motif within the Cyr61 promoter and induces Cyr61 expression. MPT, mitochondrial permeability transition; YB-1, Y-box binding protein 1; EMT, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; Cyr61, cysteine-rich protein 61; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; FGF2, fibroblast growth factor 2; PECAM, platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule; TSP-1, thrombospondin-1; SPARC, secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine; WWOX, WW domain-containing oxidoreductase; CDH4, cadherin-4; AP-1, activating protein-1; FGFR1, fibroblast growth factor receptor 1.