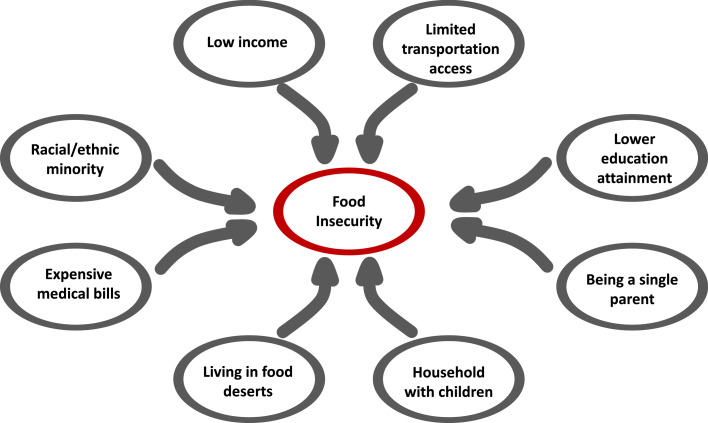
Fig. 1.
Socioeconomic Risk Factors of Food Insecurity. Multiple socioeconomic factors intersect to increase risk of food insecurity. Living in an area with limited access to nutritious food and lacking transportation can both make it difficult for families to easily purchase nutritionally adequate foods. Low educational attainment and income are associated with higher risk of food insecurity. Family structure is also an important determinant because households with children (particularly those led by single parents) are more likely to be food insecure than households without children.