Fig. 2.
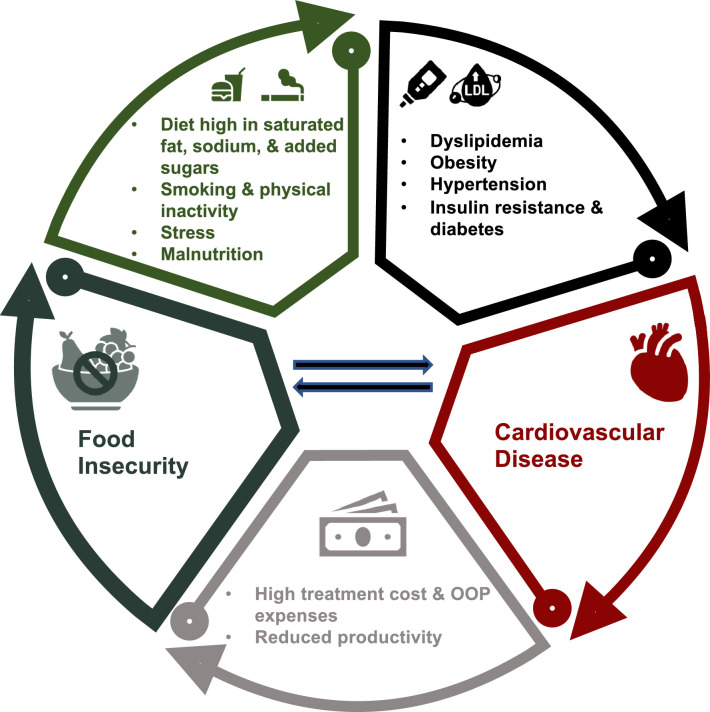
Central Illustration. The association between FI and CVD may be explained by pathways in which both conditions increase risk of the other. Food-insecure individuals may consume greater amounts of unhealthy food, including those with added sugars, high saturated fat content, and excess sodium. Individuals experiencing FI are also more likely to smoke and have low physical activity, further revealing FI's significant impact on behavioral risk factors for CVD. These lifestyle factors, combined with psychological stress and poor nutrient intake, ultimately increase risk of CVD by promoting the development of conditions such as diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. It has also been suggested that CVD can, in turn, increase patients’ risk of being food insecure due to the financial strain associated with treatment costs and reduced productivity.