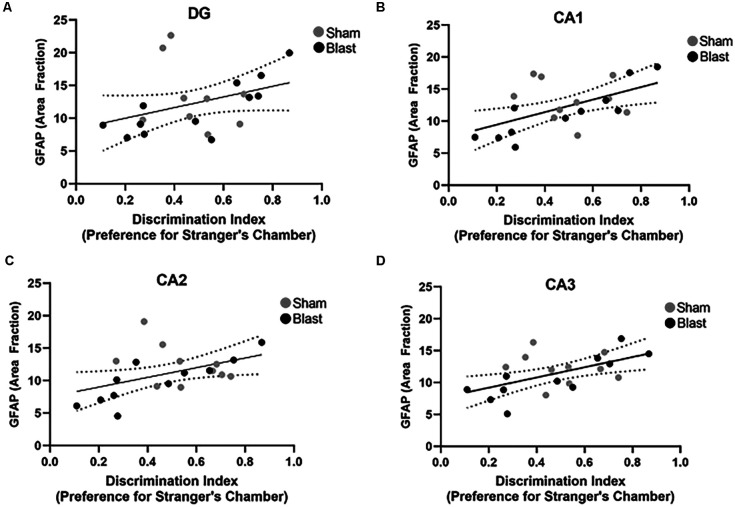
Figure 11.
Decreased GFAP expression in the hippocampus correlates with sociability deficits 52 weeks following blast injury. Pearson’s correlation analysis between the area fraction of GFAP in the hippocampus and preference for the stranger’s chamber using the three-chamber sociability test (A–D). (A) No significant correlation was found between the area fraction of GFAP in the DG and preference for the stranger’s chamber (p = 0.09, r = 0.4). (B) A significant positive correlation between the area fraction of GFAP in the CA1 and the preference for the stranger’s chamber (p = 0.009, r = 0.5). (C) A significant positive correlation was also found between the area fraction of GFAP in the CA2 and preference for the stranger’s chamber (p = 0.03, r = 0.5). (D) Correlation between the area fraction of GFAP in the CA3 and preference for the stranger’s chamber was also found to be significant (p = 0.009, r = 0.5). Overall regression lines are black with 95% confidence intervals denoted with black dotted lines.