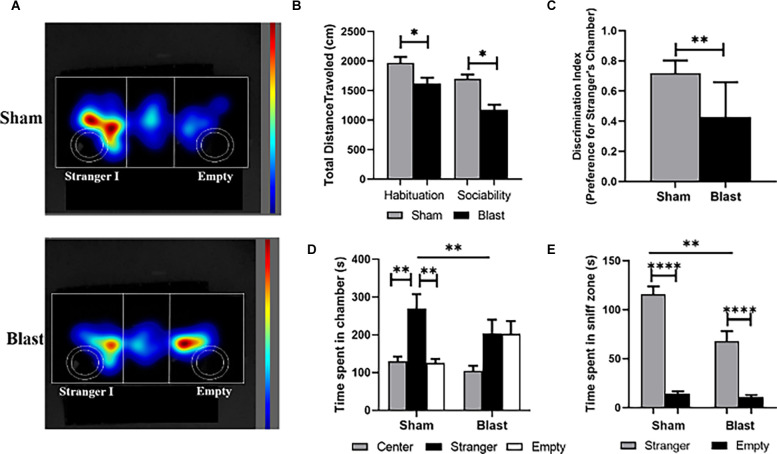
Figure 3.
Animals exhibit decreases in sociability 36 following repeated blast exposure. (A) Representative heat map images show that sham animals spent more time with stranger I, whereas blast animals spent an equal amount of time in the chamber of stranger I and the empty chamber. The circular outlines indicate the sniff zones within each chamber. (B) Total distance traveled was significantly decreased for both the habituation and sociability trial of blast animals compared to shams. (C) An average discrimination index showed that sham animals had a significant preference for the stranger’s chamber (ratio > 0.5) than blast animals (ratio < 0.5). (D) Decreased sociability in blast animals was also indicated as no significant differences being observed in time spent in the chamber of stranger I and the empty chamber. (E) While both sham and blast animals spent significantly more time in the sniff zone of stranger I than the empty sniff zone, this time was still significantly decreased in blast animals compared to shams. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001. Data is represented Mean ± SEM.