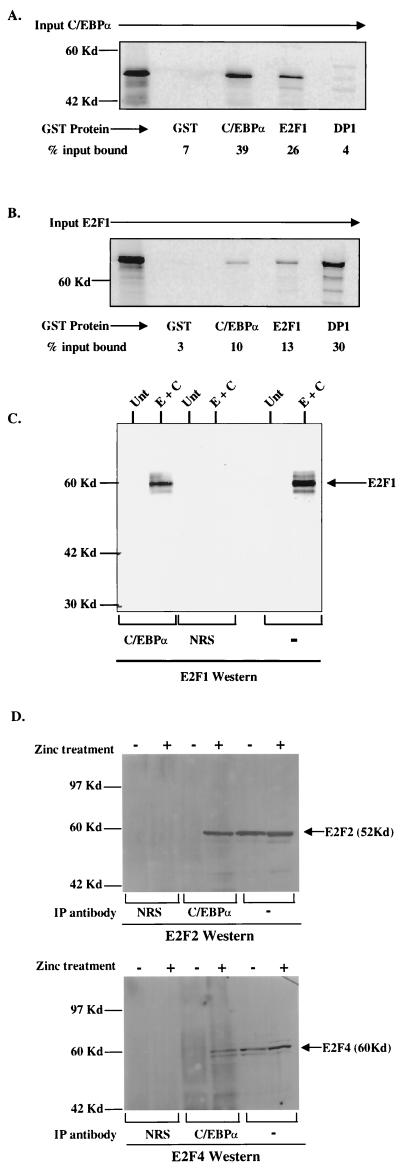
FIG. 5.
C/EBPα and E2F1 physically interact in vitro and in vivo. (A) Binding of 35S-labeled in vitro-translated C/EBPα (input C/EBPα) to GST (negative control for binding), GST-C/EBPα (positive control for binding), GST-E2F1, and GST-DP1. (B) Binding of 35S-labeled in vitro-translated E2F1 (input E2F1) to the same GST fusion proteins. Percent input bound represents the amount of in vitro-translated protein complexed with GST fusion proteins as calculated using a phosphorimager (Molecular Dynamics). (C) COS7 cells either untransfected (Unt) or transfected with E2F1 and C/EBPα expression vectors (E + C) were immunoprecipitated with C/EBPα antisera or control NRS followed by Western analysis with E2F1 antibody. As a control for E2F1 expression and migration, 1/30 of the COS7 lysate used for immunoprecipitation was resolved by SDS-PAGE (marked “−” for immunoprecipitation antibody). The position of E2F1 is indicated. (D) C/EBPα interacts with endogenous E2F proteins in myeloid cells. Uninduced (−) or induced (+) U937α#2 cells were immunoprecipitated (IP antibody) with C/EBPα antisera or control NRS followed by Western analysis with either E2F2 or E2F4 antibody. As a control for E2F2 and E2F4 expression and migration, 1/30 of the lysate used for immunoprecipitation was resolved by SDS-PAGE (marked “−” for immunoprecipitation antibody). The positions of E2F2 and E2F4 are indicated.