FIG. 8.
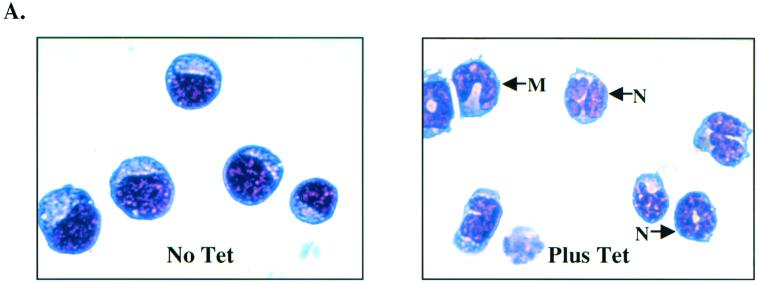
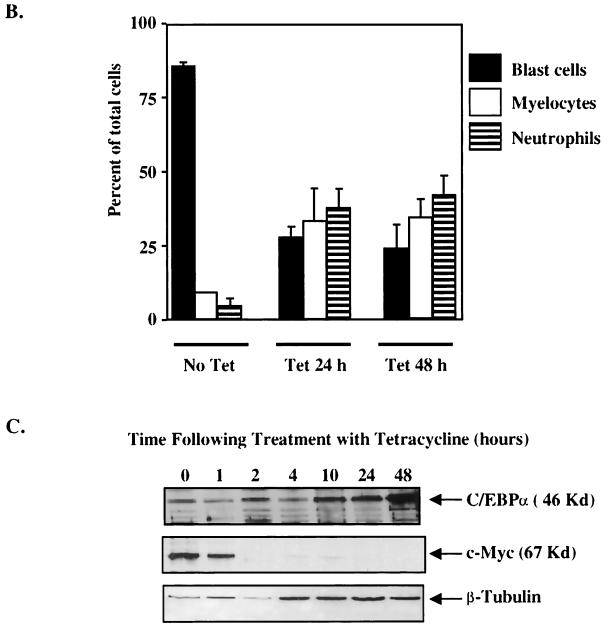
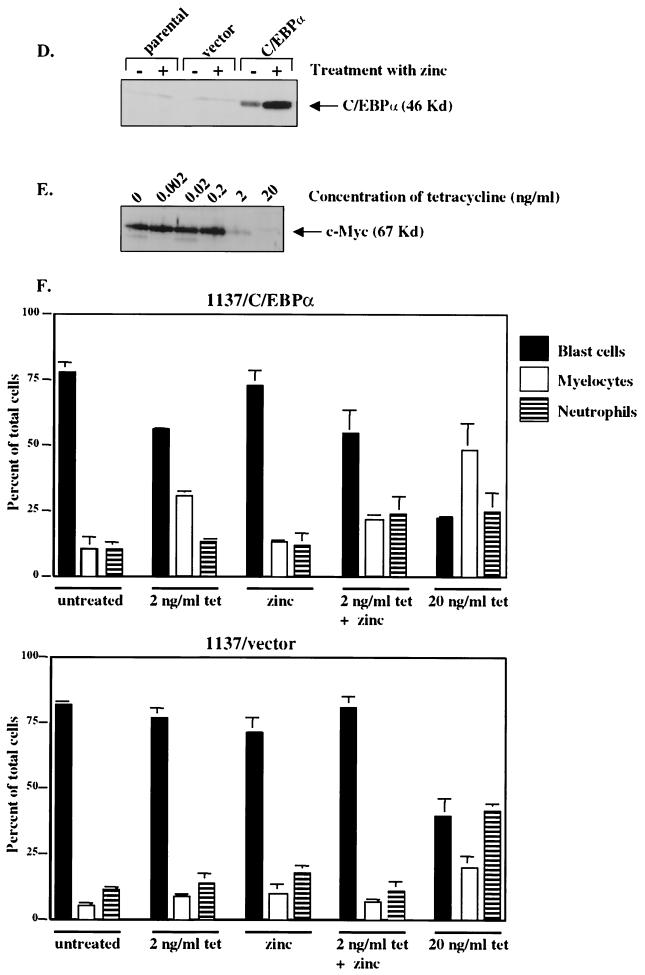
Down-regulation of c-Myc is crucial to the granulocytic differentiation pathway. The 1137 cell line was derived from murine bone marrow of a transgenic line with a human c-Myc cDNA under the control of a tetracycline-responsive promoter. The addition of tetracycline to the culture medium turns off human c-Myc expression, resulting in the differentiation of these myeloblasts to neutrophils. (A) Wright-Giemsa-stained cells without (No Tet) or with (Plus Tet) treatment with tetracycline. Cells treated with tetracycline differentiated into myelocytes (M) and neutrophils (N). (B) Differential analysis of Wright-Giemsa-stained slides following treatment with tetracycline for 0, 24, and 48 h, respectively. (C) 1137 cells were harvested for cell lysates to use in Western blotting at indicated time points following treatment with tetracycline. (Top) Western blot hybridized with C/EBPα antiserum shows that the level of endogenous C/EBPα protein increased 24 h following treatment with tetracycline. This corresponds to the shift to mature cells seen in panels A and B. (Middle) The same blot hybridized with c-Myc antiserum, showing that c-Myc protein levels dramatically decreased 2 h following treatment with tetracycline. (Bottom) The same blot hybridized with a β-tubulin antibody to control for protein loading and integrity. (D) Western analysis of 1137 stable lines with (+) and without (−) treatment with zinc. “parental” indicates the 1137 parental line, “vector” indicates the 1137 stable line with metallothionein vector, and “C/EBPα ” indicates the 1137 line with metallothionein-driven C/EBPα. (E) Western analysis of cell lysates prepared from the 1137/C/EBPα stable line with the indicated treatment with tetracycline. The level of human c-Myc protein was titrated by 100-fold dilutions of tetracycline. A 20-ng/ml concentration turns off c-Myc expression, while a 2-ng/ml concentration results in a low level of c-Myc expression. Lower concentrations of tetracycline result in no decrease in c-Myc protein expression. (F) Differential analysis of Wright-Giemsa-stained slides following treatment of 1137 stable lines with tetracycline, zinc, or the combination of tetracycline and zinc for 48 h.