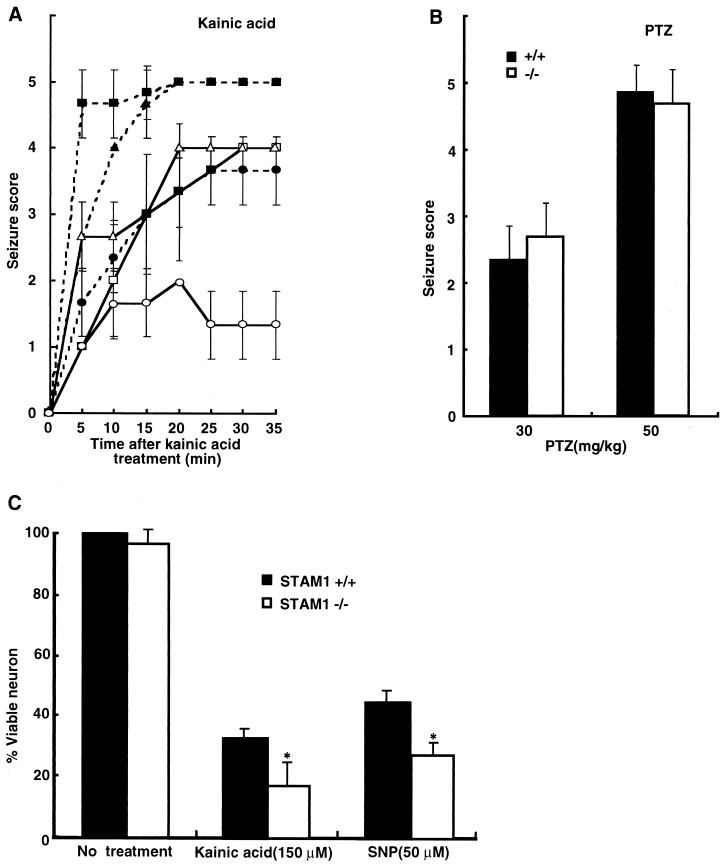
FIG. 7.
Susceptibility to kainic acid-induced seizures of STAM1−/− mice. (A and B) Scores for seizures induced by kainic acid and PTZ. Four-week-old C57BL/6-STAM1+/+ (open symbols in A) and C57BL/6-STAM1−/− (filled symbols in A) mice were injected intraperitoneally with kainic acid (A) at doses of 10 (circles), 20 (triangles), and 30 (squares) mg per kg of body weight and with PTZ (B) at 30 and 50 mg per kg. Seizures were scored as follows: 1, arrest of motion; 2, myoclonic jerks of the head and neck with brief twitching movements; 3, unilateral clonic activity; 4, bilateral forelimb tonic and clonic activities; and 5, generalized tonic and clonic activities with loss of posture and death from continuous convulsions. At least six mice in each group were observed and scored to derive the temporal response curve. PTZ provoked rapid and abrupt general tonic-clonic convulsions, so the same criteria were used to record the PTZ-induced seizures within 5 min of injection. (C) Vulnerability of STAM1−/− primary hippocampal neurons to cell death induced by kainic acid and an NO donor. Hippocampal neurons were isolated from C57BL/6-STAM1+/+ and C57BL/6-STAM1−/− embryos at E18.5. Cultured neurons were treated with 150 μM kainic acid or 50 μM SNP. After 24 h, they were examined for cell viability by the Alamar blue assay. Data represent means and standard errors for three independent experiments performed in triplicate. An asterisk indicates a P value of <0.01 for a comparison with the wild type.