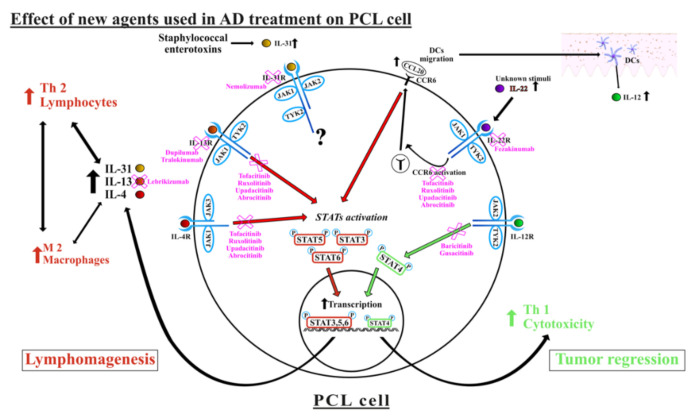
Figure 1.
The influence of agents targeting interleukins (IL) 4, 13, 22, and 31 and JAK/STAT pathways on the primary cutaneous lymphomas (PCLs) cells and tumorous microenvironment. The up and down arrows stand for increase/decrease of the interleukins concentration, cell count or receptor’s upregulation. IL-12 promotes phosphorylation of STAT4, thereby stimulating the cytotoxic mediated CD8(+) answer. Concomitantly, IL-4, IL-13, and IL-31 contribute to forming the Th-2 cytokine profile, which results in decreased cytotoxic immunosurveillance and lymphomagenesis. IL-4, IL-13, and IL-22 activate different Janus kinases, which promote the STAT3, STAT5, and STAT6 activation contributing to the transcription of pro-tumorous factors. In the advanced stages of the disease, this phenomenon may be seen more prominently. By blocking several pathways or cytokines, biologic drugs and small molecule inhibitors may affect both the malignant microenvironment and pathways in the PCLs cells.