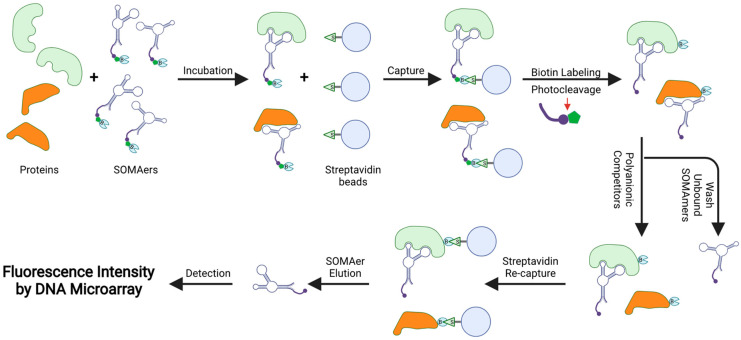
Figure 5.
Schematic overview of the SOMAscan analysis. Each SOMAmer contains a biotin (B) group, a photo-cleavable link, and a fluorescent tag at the 5′ end. SOMAmers are mixed with the test sample, forming SOMAmer–protein complexes. The complexes are captured on streptavidin beads via strong biotin–streptavidin interaction. The captured proteins are then biotinylated and the SOMAmer–protein complexes are released from beads using ultraviolet light. Polyanionic competitors are added to promote the dissociation between proteins and non-specific SOMAmers. The SOMAmer–protein complexes are recaptured on new streptavidin beads. Protein-bound SOMAmers are eluted, hybridized to custom arrays of SOMAmer-complementary oligonucleotides, and quantified by fluorescence intensities, which are proportional to the concentrations of their cognate target proteins.