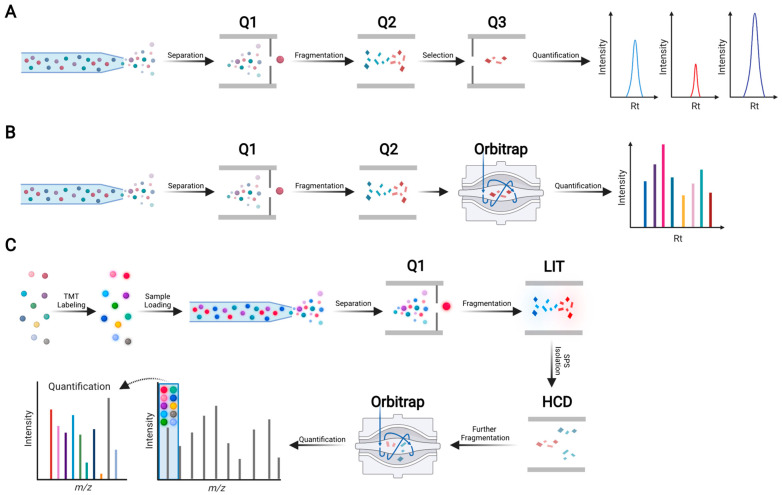
Figure 7.
Schematic overview of MS-based targeted proteomics methods. (A) Schematic of selected reaction monitoring (SRM), also known as multiple reaction monitoring (MRM). For peptide quantification, three to five selected fragment ions from a single peptide precursor ion are measured sequentially. SRM is typically performed on a triple quadrupole (QqQ) mass spectrometer. The first quadrupole (Q1) isolates a predefined peptide precursor ion, the second quadrupole (Q2) is a collision cell where isolated precursor ions are broken into product ions (also called fragment ions), and the third quadrupole (Q3) isolates predefined product ions. Such predefined pairs of precursor and product ions are called transitions, which provide high specificity and sensitivity to quantify peptides that are surrogates of proteins of interest. (B) Schematic of parallel monitoring reaction (PRM). PRM employs a high-resolution Orbitrap mass analyzer to simultaneously monitor many product ions. Because transitions do not need to be defined in advance, PRM is easier to set up than SRM. (C) Schematic of TOMAHAQ (triggers by offset, multiplexed, accurate mass, high-resolution, absolute quantification). Peptides derived from 10 (or 16) samples are labeled with 10-plex (or 16-plex) tandem mass tag (TMT) reagents, which consist of 10 (or 16) different isobaric compounds with the same mass and chemical structure. Subsequently, an equal amount of differentially TMT-labeled peptides is pooled into one tube, followed by LC separation and targeted MS analysis. Rt: retention time; LIT: linear ion trap; HCD: higher-energy collisional dissociation.