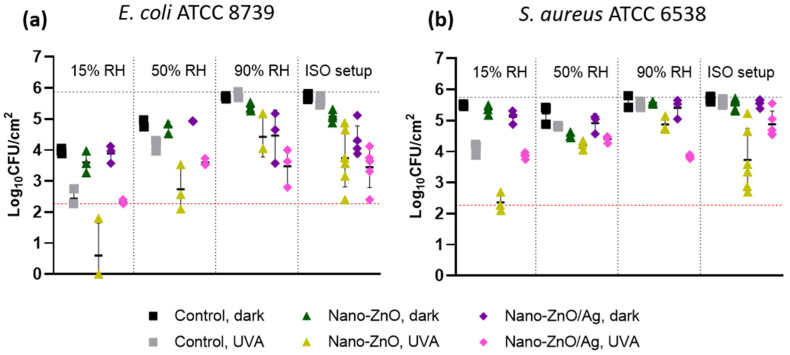
Figure 6.
Antibacterial activity of surfaces based on matrix-embedded nano-ZnO or nano-ZnO/Ag towards E. coli (a) and S. aureus (b) in different relative air humidity (RH) conditions after 1 h. Nano-enabled surfaces generally demonstrate higher antibacterial ability at higher RH compared to the control surface in the same conditions; however, the effect of these surfaces is dependent on RH. Nano-Ag/ZnO surfaces lose their antibacterial activity at low RH in dark conditions (dark blue; a). UVA exposure is more toxic to both bacteria at lower RH and E. coli is more sensitive to drying at lower RH. Mean value of at least 3 experiments ±SD is presented. Red dotted line denotes the practical limit of quantification with 3 colonies counted in undiluted samples.