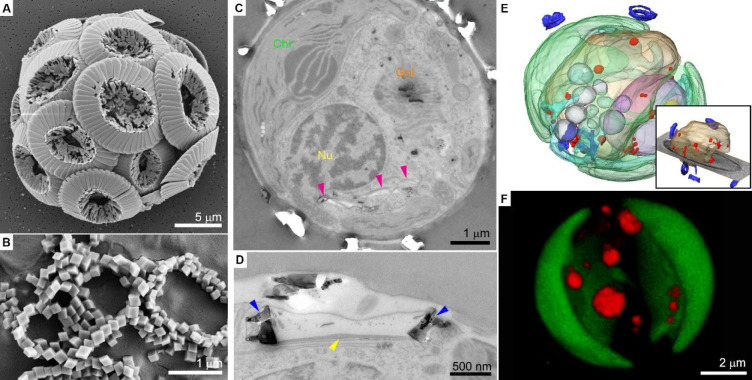
Figure 1.
Formation of coccoliths. (A,B) SEM images of Coccolithus braarudii coccoliths. The diploid life stage forms intricate crystal morphologies (A), while the haploid stage forms simple rhombohedral crystals (B). (C–F) Cellular anatomy of Pleurochrysis carterae. (C, D) Sections in fixed cells show in (C) the various cell organelles (Chl., chloroplast; Nu., nucleus; magenta arrowheads indicate coccolith vesicles), and a high magnification image shows in (D) a coccolith vesicle (blue arrowheads indicate the crystals, yellow arrowhead indicates the organic base plate). Reprinted with permission from ref (22). Copyright 2020 Elsevier. (E) 3D rendering of a cryo-fixed cell. The inset shows the vacuole (light brown) filled with Ca–P-rich bodies (red) and coccoliths (blue). (F) 3D rendering of a live cell using confocal microscopy, showing several dense intracellular pools stained with DAPI (red); chloroplasts are in green. Reprinted with permission from ref (18). Copyright 2021 Wiley-VCH GmbH.